Updated: June 9, 2023.
The full guide to the crawl budget and the crawl budget optimization with tons of pro tips.
If you have been in SEO for some time, you have probably heard about both the crawl budget and crawl budget optimization. But is this topic an important area of technical SEO? Is crawl budget optimization something you should worry about? Let’s find this out!
Google crawl budget is the number of resources Google uses to crawl a website. In other words, it describes the number and frequency of times that Google decides to search for pages on a website.
In this guide, you will learn what crawl budget is, what factors influence crawl budget, why crawl budget is important for SEO, how to optimize crawl budget for better SEO results, and more!

❓Looking to hire someone to audit your website or do SEO? Make sure to check the SEO services I offer including SEO consultations and monthly SEO services.
👉 Contact me for more information or if you have any questions or learn more about why you want to hire me as your SEO consultant.
What is Google Crawl Budget?
There are really a lot of different definitions of crawl budget and it is hard to pick just one. In addition, there are a few other terms that go hand in hand with the crawl budget.
Here are the most important ones:
- Google crawl budget is the number of URLs that Googlebot is able to crawl and wants to crawl.
- Crawl demand – which is about how much Google wants to crawl the web pages of a site – is an important part of the crawl budget. Here is a handy definition of the crawl demand from the Google Search Central documentation on the crawl budget.
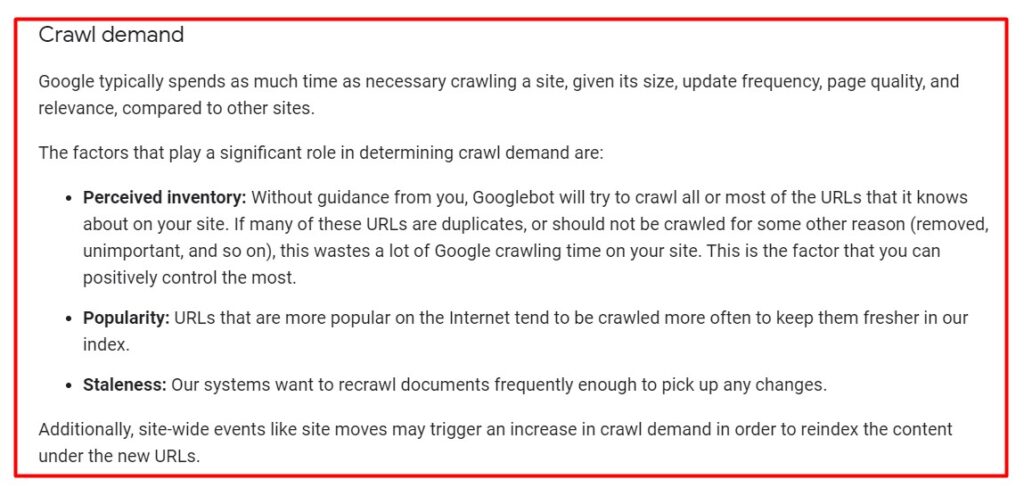
- Crawl rate limit – which is supposed to limit how much Google crawls the site so as not to overload its server – is also an important component of the crawl budget. The crawl rate limit is dependent on the following three factors also listed in the Google Search Central documentation.

- Crawl budget is something that smaller sites (below a few thousand URLs) usually do not need to worry about (more about that later).
⚡ Make sure to check my in-depth guide on how to do an SEO audit and my list of 99 SEO mistakes.
Is crawl budget optimization important?
Here are the reasons why you want to care about the crawl budget of your site:
- You want search engines to locate and understand as many indexable pages of yours as possible, and you want them to do so in the quickest manner possible.
- You want search engines to pick up new pages you add and existing ones you update, and you want that done as soon as possible. If they index the pages sooner, you will benefit from them sooner.
- Search engines will not be able to crawl your website efficiently if you waste your crawl budget. They will spend time on areas of your site that are irrelevant, which is something that can lead to important parts of your website being left undiscovered. They won’t crawl and index these pages if they do not know about them, and you will not be in a position to bring visitors to them through search engines.
- Wasting the crawl budget is harmful to the site’s SEO performance.
When should you care about the crawl budget?
And here is when you should really worry about the crawl budget of your site:
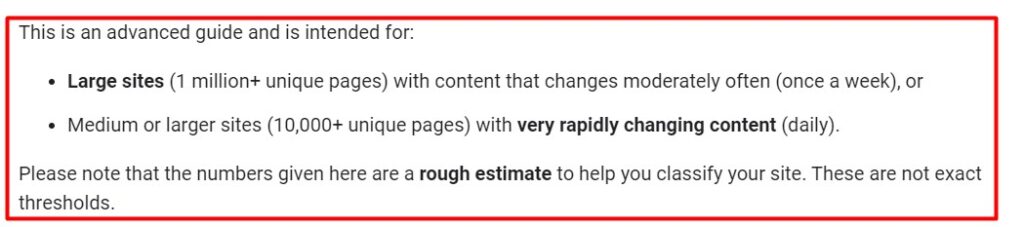
- The crawl budget, generally speaking, is only something you need to worry about if you have a large website, for example, 10,000+ pages. Here is what the Google documentation says about it.
- The crawl budget quickly becomes tight for the websites which make daily changes or have a large number of subpages that don’t need to be crawled.
- This has a particular impact on online shops with thousands of products, numerous product categories, wish lists, recommendation lists, filter options, search functions, etc. as ones that fit that category.
- With regards to issues of indexing duration, it makes sense to take a look at your crawl budget if you notice that new pages or updated content are taking a long time to be indexed to find a potential solution.
The Main Factors That Influence The Crawl Budget
There are several factors that affect the crawl budget. Most of them can have a negative impact on the crawl budget.
Here are the factors to consider and pay attention to with regards to the crawl budget:
- When a Googlebot crawls your website, it is important that all pages offer added value. A problem often arises when a website contains too many low-quality web pages.
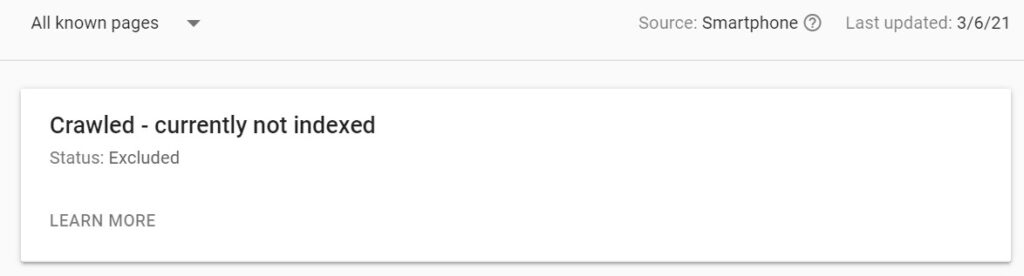
- Because of the crawl limit, not all pages of the website may be crawled and therefore indexed. This can then translate to getting less traffic. Here is the definition of the crawl limit from the Google documentation.

- In this context, you should also think about the crawl rate, which is the crawling frequency that describes the number of requests per second that the Googlebot makes to your website during the crawling process, for example, five requests per second.
The crawl rate is simply:- The number of connections used by the spider to crawl a website.
- The time elapsed between visits to a web page.
- If a website reacts very fast, the crawler assumes that the servers are running properly. However, a problem may occur when a website reacts slowly. As a result, this will reduce the crawl rate for this website.
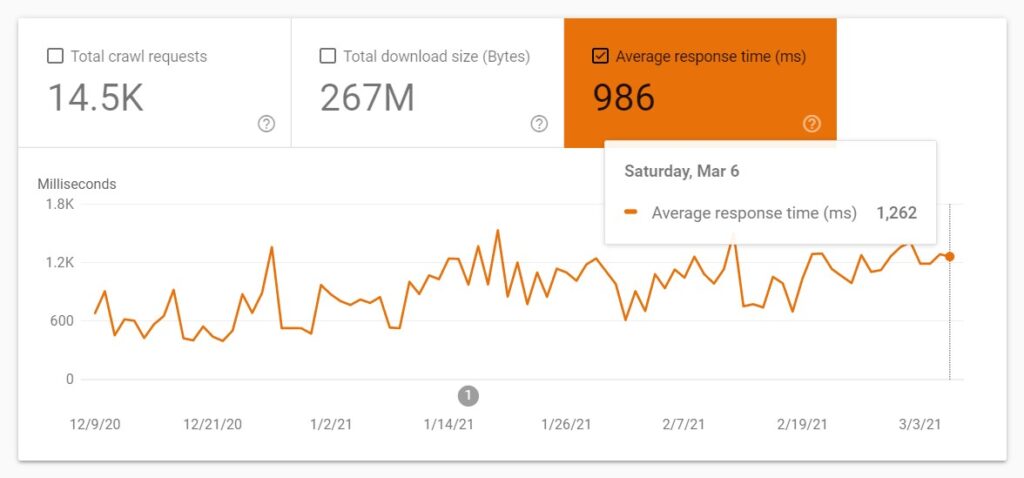
- Crawl health refers to how fast or slow a website reacts. Here is how Google defines it.

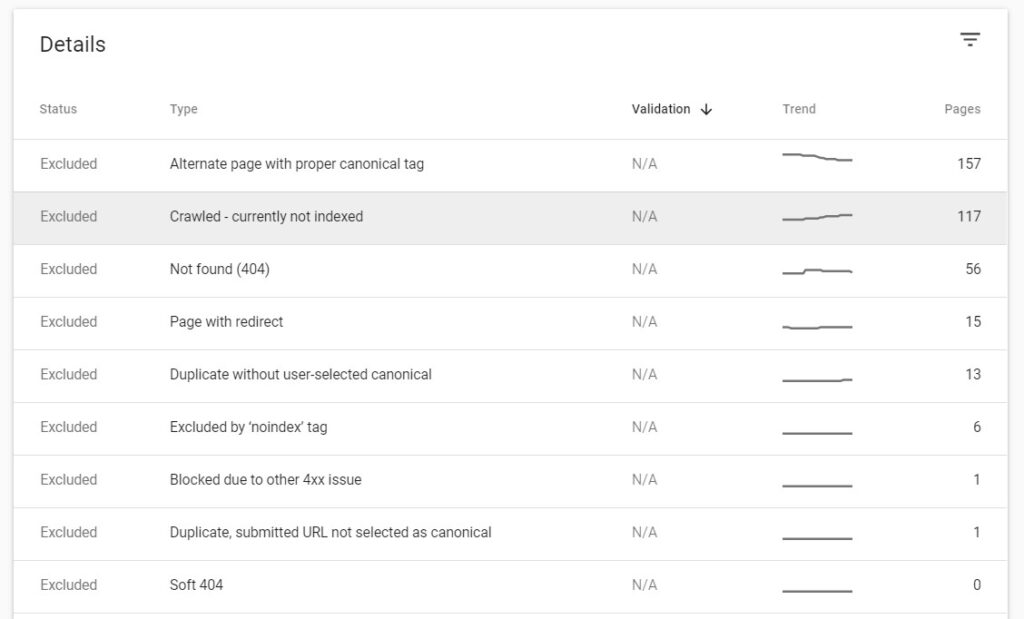
- In this regard, the term index budget is also important. It records how many of the crawled pages are actually indexed. Since most pages give the 404 response and therefore cannot be indexed, the index budget is not going to be used.
What Other Factors Influence the Crawl Budget
The following factors influence the website’s crawl budget:
- Link authority: Backlinks from big and relevant websites are an important factor that can have a positive impact on the crawl budget. In this context, Google tends to crawl popular links on the internet more often to keep them fresher in their index.
- Content: Scope and freshness of the content. This includes both the total number of documents that can be indexed and the interval at which new content is added to the website.
- Prioritizing content: Important content should receive the most links, both internally and externally. This helps the crawler quickly identify and process important documents.
- Control indexing: Not all pages need to be included in the index. By excluding some subpages, you can direct the page crawler to important pages that you want to be indexed first.
- Speed: Google likes fast websites. Therefore, it should be the priority of every webmaster to have their website load as fast as possible.
⚡ Make sure to check my Google page experience audit and Core Web Vitals audit to learn how to optimize your site for Google page experience signals.
How To Check What Resources Google Is Crawling
There are basically two ways in which you can check what resources Google is crawling so that you can determine whether the crawl budget is being wasted: do a log file analysis or/and analyze the Crawl Stats report available in Google Search Console.
Do a log file analysis
Doing a log file analysis is the best way to learn how Google is crawling your site and whether it is crawling some resources unnecessarily. You can either do the “raw” log file analysis using an Excel spreadsheet or use a tool that will analyze the data for you. I like to use the Semrush Log File Analyzer.
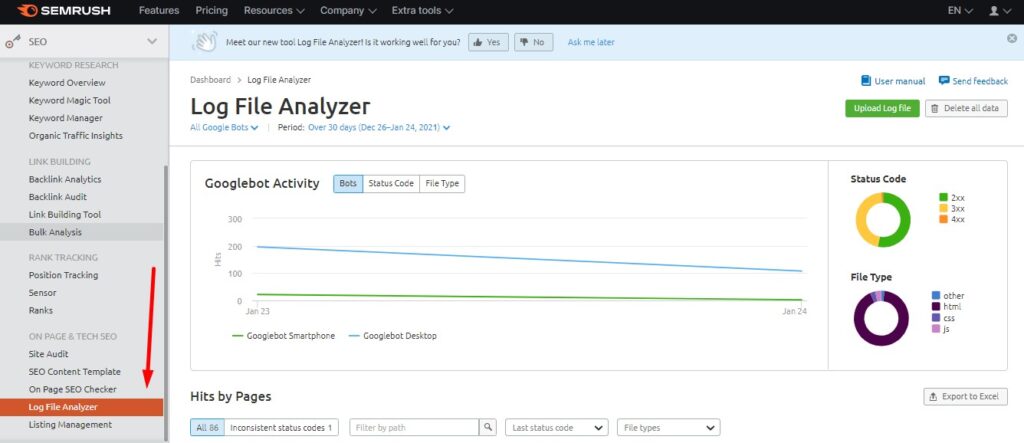
⚡ Check my guide on how to do a log file analysis with JetOctopus.
Check the GSC crawl stats report
The Google Search Console crawl stats report is not as detailed as a log file analysis but it can still provide a good insight into how the Googlebot is crawling your site. You can access the report by going to Settings > Crawl stats > OPEN REPORT.
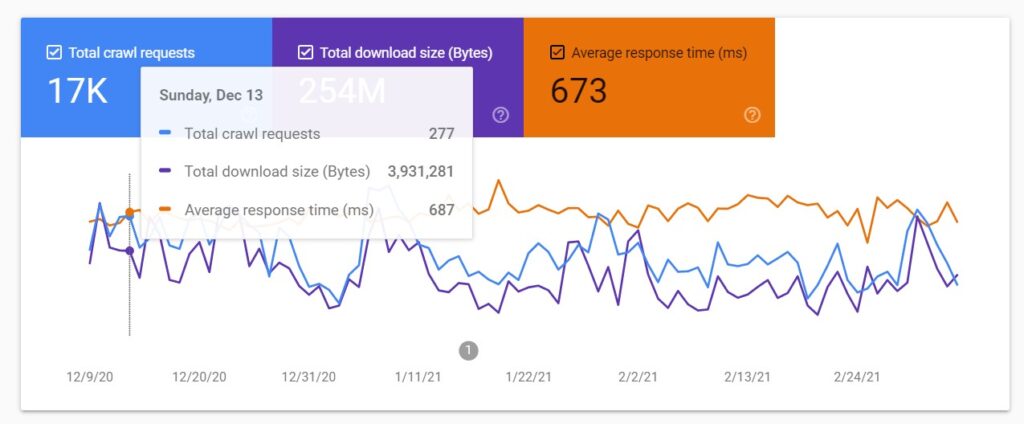
⚡ Check my in-depth guide to the Google Search Console crawl stats report to learn how to use and analyze the data provided by the tool.
Why is Google Crawl Budget Important for SEO?
Google Crawl Budget is important for SEO because if the crawler is busy with a lot of irrelevant files, there may not be enough budget left for “good” and important pages.
For example, an online shop that has 10,000 product detail pages requires a single request for each. Every page “weighs” several megabytes. The crawler will crawl these pages and will eat up a certain – possibly very large – part of the crawl budget. If you then add new products, they may be indexed a lot later.
Here is what you should know and do:
- You should ensure that you don’t have irrelevant content crawled by Google.
- Google doesn’t notify you when it’s busy with too many irrelevant pages.
- When it comes to the impact of crawling on your rankings, you shouldn’t be worried as it has none.
- If your crawl budget is insufficient, changes and new content will be added to the index with a delay. In the worst-case scenario, this can lead to a missed opportunity for traffic and sales.
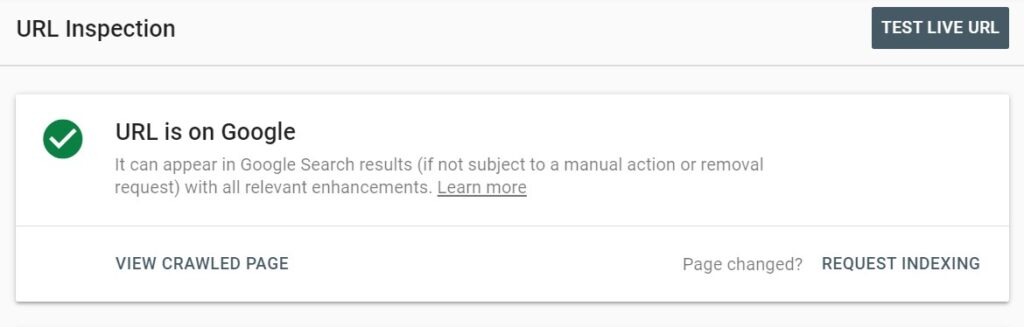
- You can let Google know about individual pages that you want to be crawled quickly (for example, updated articles) using the Google Search Console URL Inspection tool. Here is how to do it:
- Go to the Inspection URL tool in Google Search Console and enter the URL you want to get crawled quickly. Next Click on REQUEST INDEXING and Google will add the URL to the crawl priority queue.
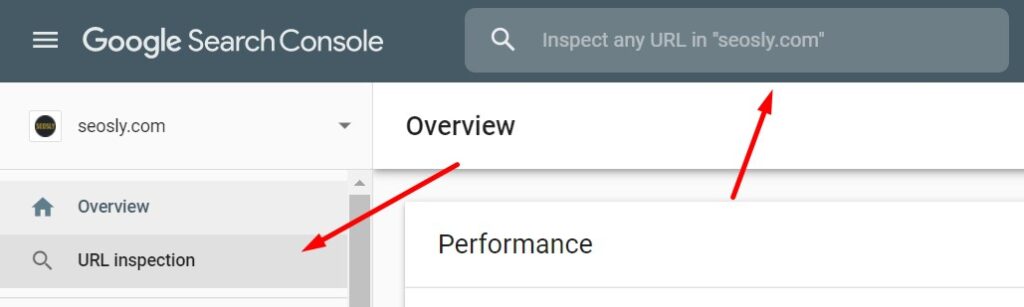
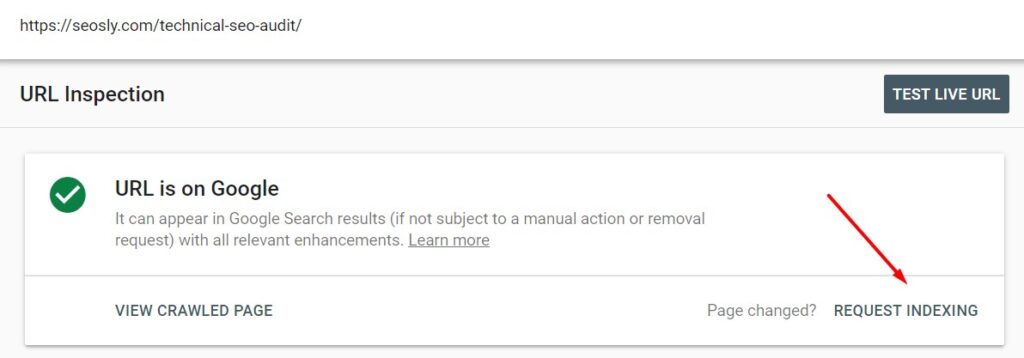
In many cases, you may see the changes after a few minutes.
⚡ Check my on-page SEO checklist (500+ pro SEO tips) to learn about all the most important on-page factors you should take into account when analyzing a website.
How to Optimize Crawl Budget
Optimizing the crawl budget means making the most of the short amount of time that Googlebot devotes to your site.
Let’s take a look at a practical example.
If you have pages on your website that do not add value to your users, you run the risk of the Googlebot losing valuable time. The negative impact of this is easy to pinpoint. Not only is the risk of lost valuable time is something to scoff at in and of itself but also if the risk unfortunately materializes, that means you will have missed out on an opportunity for Googlebot to actually focus on the web pages that actually bring added value to the table.
It goes without saying that you want to avoid this potential scenario as much and as often as you can.
Here is what you need to keep in mind:
- Remember that a website with continuously updated content will be increasing its crawl budget.
- In contrast, poor quality, outdated, duplicate content, and 404 pages reduce the crawl budget.
- While it may seem obvious, creating bad content is counterproductive. There is the risk that Googlebot will waste time scanning poor-quality pages instead of scanning the high-quality pages.
- Googlebot is already pretty good at its job, but you can still help it by keeping your content up to date and of high quality!
There are two ways in which you can optimize or improve the crawl budget for your site:
- You can increase the crawl budget by improving your site.
- You can reduce the time between scans.
The below 12 best crawl budget optimization techniques and tips will help you do just that.
1. Optimize the speed and performance of your site
Increasing your page speed is the first way to optimize the crawl budget of a website. A long loading time always means that the data will be downloaded way more slowly.
Not only does a poor website speed lead to a bad user experience, but also it has a negative impact on the crawl budget. The crawl budget, as already mentioned, is a time budget.
If Googlebot has to process large amounts of data per page, then it will reduce the number of pages that can be crawled in a given time window.
⚡ One of the best ways to quickly improve the speed of a WordPress site is to install WP Rocket, a WordPress plugin to speed up the site in just one click.
In this regard, the speed of the server is crucial. If you optimize the download time of your page, Googlebot will have more time for other pages. Here are some tips for you to consider:
- Invest in a quality server.
- Optimize the source code to make it “readable” for the web crawler. If your HTML code contains a lot of extra text, the crawler might have a hard time determining if your page is relevant to a specific query.
- Compress images on your page without sacrificing quality.
- Optimize the website for Core Web Vitals (guide) which are currently the best set of metrics that influence the speed and performance of a website.
- Use tools, such as Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse to analyze the speed and performance of your site.
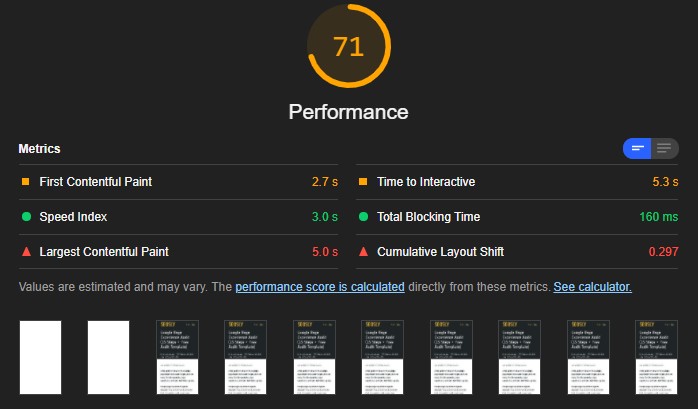
⚡ Check my Core Web Vitals audit to learn about the ways you can fix the performance and speed issues of a website.
2. Improve the structure of the website
A clear and linear structure of the pages on your website will help the website maximally use its crawl budget. This will allow Googlebot to scan and index any new or updated web pages without any problems.
Here are some of the best practices regarding the site structure:
- Follow the famous three-click rule, which states that any user should be able to get from any page of your site to another with a maximum of three clicks.
- You can use Screaming Frog SEO Spider to analyze the structure and crawl depth of your site. The tool will also show you any orphaned pages.
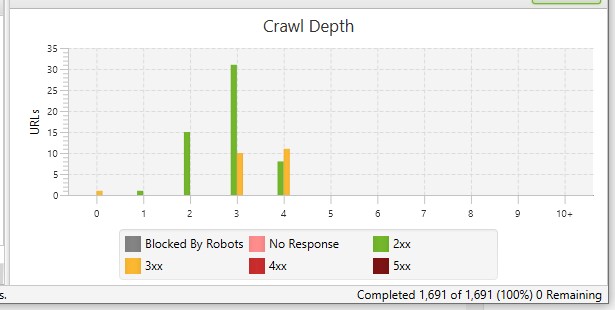
- Avoid “dead end” or orphaned pages which are the pages that do not contain any internal or external links.
- Use canonical URLs in the XML sitemap. Even if it does not directly influence the crawl budget, it can help Google understand which pages it should crawl and index.
3. Use the power of internal linking
A good internal linking structure makes it easy for crawlers to navigate the website and identify its structure, context, and key landing pages.
- A lot of internal links pointing to a given web page indicate that this is a relatively important web page of the website.
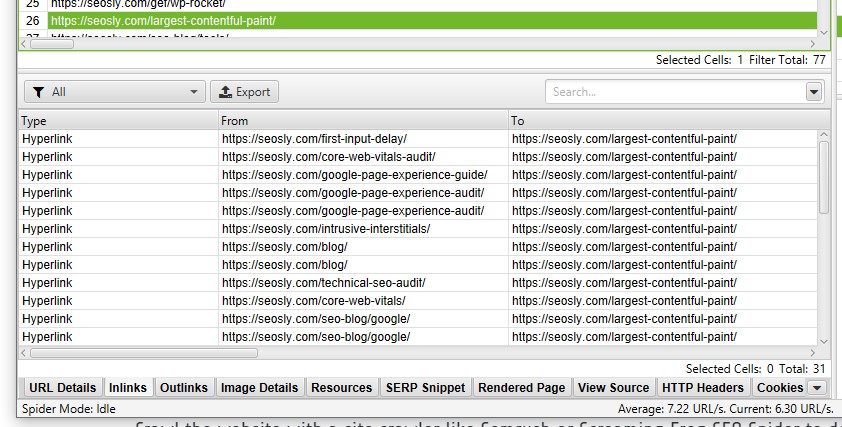
- Internal links allow the crawlers to reach the relevant web pages that should be indexed and then – hopefully – ranked highly in SERPs.
- A good structure of internal links reduces the number of the so-called “orphan pages”, sub-pages that are difficult to reach due to a lack of external and internal links.
4. Fix broken links
Not only can broken links have a negative influence on the site’s rankings, but also they waste the site’s precious crawl budget. Here is what you should do:
- Crawl the website with a site crawler like Semrush or Screaming Frog SEO Spider to detect any 404 web pages.
- Either restore the 404 web pages or remove the links pointing to them. You can also replace broken links with working links.
5. Use nofollow links
With nofollow links, you tell Googlebot not to waste time scanning certain pages. These pages can either be less important or ones that are already linked within another topic.
- Consider nofollowing the links to web pages that you do not want Googlebot to crawl. Remember, however, that Google treats nofollow links only as hints (not directives).
- That way, obviously, you will waste neither budget nor time, thus ensuring that the scan is instead dealing with parts of the site that really need to be crawled.
- A good example for this is faceted navigation links. This is any page that has two or more facets indexed. When you make all the internal links pointing to those pages “nofollow” you help save crawl budget and maintain link equity.
6. Optimize robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a powerful tool to free up room for relevant crawls. The robots.txt controls the crawler’s behavior on your website.
It defines which pages, directories, or areas are blocked for crawlers and which ones they are allowed to visit. You may discover pages that are unnecessarily crawled and thus waste valuable crawl budget.
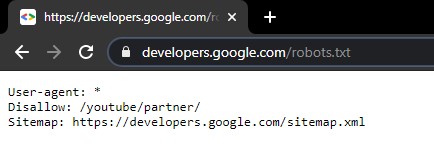
- Make sure to use robots.txt to block the resources you do not want Google to crawl.
- Remember that blocking a page in robots.txt does not prevent it from being indexed.
⚡ If you are using WordPress, you might want to learn how to access robots.txt in WordPress.
7. Update existing content
It cannot be emphasized enough. Updating your content means Google spends more time on your website.
Though you could continue to write and produce more content, that is complicated and takes a lot of time. Instead, you can simply update your old content. Not only does it take less work, but also it produces faster results.
- If you want to boost the effectiveness of your efforts from an SEO standpoint and increase your search engine traffic, it’s simple – update your old content and give yourself an improved freshness score.
- You get a traffic spike when you tell Google that your content is new. It will make the small amount of work it takes well worth it.
- If Google notices a change in your content, your site will likely be recrawled. Should it find improvements in your content, Googlebot may give you a higher budget.
8. Add new content
It’s simple – the more content you add to the website, the more often Googlebot will want to crawl your site.
- New content means adding new pages. Doing so has many benefits. For example, it can help your website rank for more keywords, boosting SEO for keywords in relation to the website’s industry.
- Also, new content on brand new website pages helps your site target a wider keyword range. That, in turn, allows websites to target more long-tail keywords and phrases related to their business.
- Moreover, new content pages create new links for your website for purposes of internal and external linking. It also helps you rank for more keywords it also increases your crawl budget by keeping your content fresh.
- However, that freshness can in fact decrease over time. In other words, Google will give the content an initial boost when it’s published for the first time, but its SEO, over time, goes down. That is why it is important to continue to add fresh content and make it a regular part of your content strategy.
9. Delete duplicate content
If you remove all the pages that are no longer relevant, you won’t be wasting the crawl budget allocated for your site.
- But if you don’t want to remove this content entirely, you can think about merging it with the existing high-quality web pages.
- If you decide to do that, do not forget about internal links. If a link refers to a page that you are about to delete, you have two options. You can either implement a 301 redirect that tells the search engine the page is accessible from a different URL, or you can change the link URL on the linking web page.
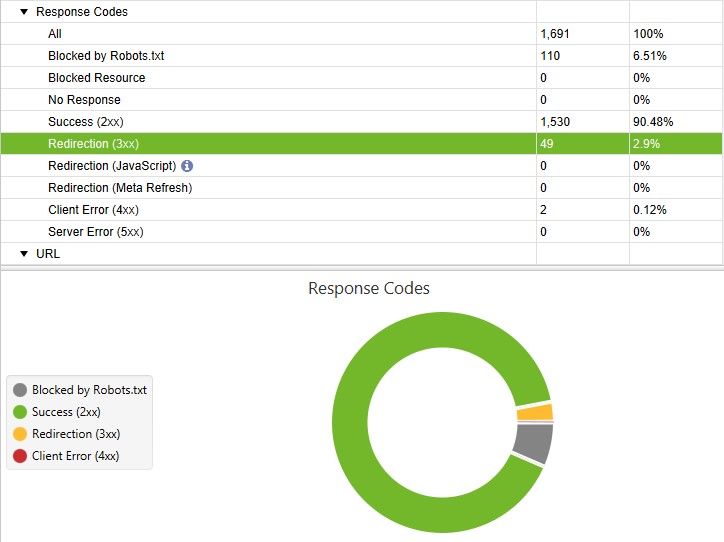
10. Serve the correct status codes
Every redirect or a 404 page uses up the crawl budget allocated for the web page. Not only do error pages have a serious impact on user experience, but they will also be unnecessarily crawled.
- Redirects are completely normal and cannot be avoided. However, you should make sure that you keep them to a minimum and that there are no redirect chains.
- Redirect chains create a long path for the crawler to get to the final link target. After three jumps or more, Googlebot may stop crawling the chain. The best thing to do is avoid any redirect chains.
- If you remove web pages from your website, use a site crawler like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or Semrush to identify internal links that point to the removed page and update them so that they indicate an existing web page.
- In the event of redirect chains, remove any redirects that are in between. Page A should redirect directly to page B without any other page in between.
- You should make sure that the majority of your URLs have the status code 200 = OK. Then everything is fine.
- 404 pages are dead ends for the crawler and the user. Check your page regularly for 404 errors and fix them as soon as possible.
- Redirects (301 redirects) are also fine, as long as you use them in a crawler-friendly manner.
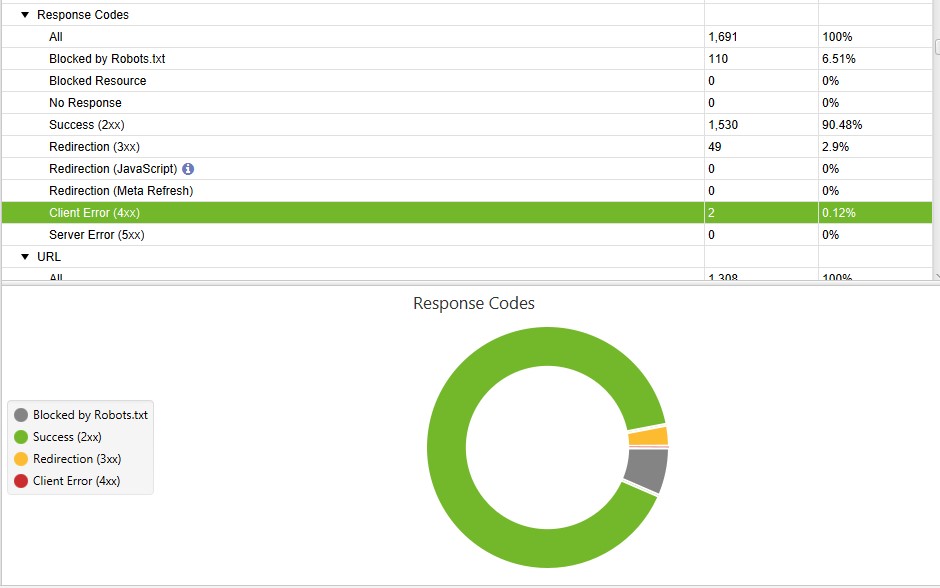
You can assess how the crawl budget is being distributed across the different pages on your site by grouping your log file data by status code. This gives you the highest overview of how much of a search engine’s crawl budget is spent on important 200 pages, as well as how much is being wasted on error pages and redirects.
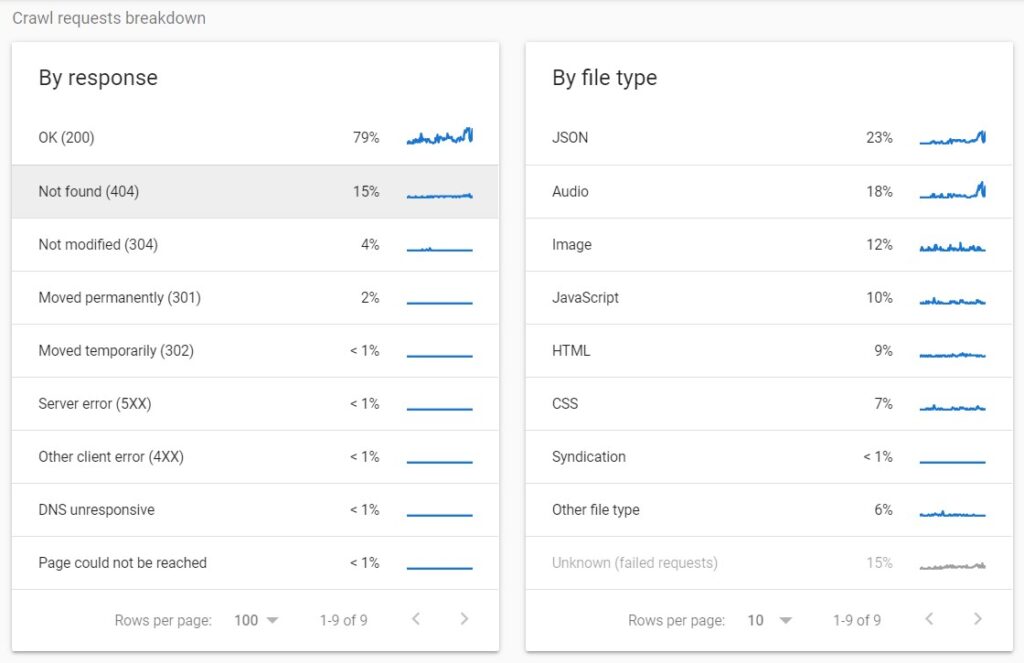
Using these data, these are some of the steps that you can take in order to improve the crawl budget across your site:
- Analyze the 200 status code URLs in order to identify any that don’t need to be crawled.
- Add disallow rules to your robots.txt file for non-essential pages with 200 status codes in order to make them inaccessible to crawlers.
- Remove internal links to 404 pages, as well redirect them where that is necessary.
- Remove all status code pages that are non-200 from XML sitemaps. Check my guide on how to find the sitemap of a website.
- Fix redirect chains in order to ensure there is only one step in each redirect being accessed by search engine crawlers and users.
How to reduce the time between crawls
If you update your content regularly, you will see an increase in the Googlebot crawling activity. Every time the web crawler visits a page and finds revised content, your crawl budget increases.
When it comes to determining the optimal crawl speed for a site, Google has sophisticated algorithms. Their goal is to crawl as many pages from sites as they can on each visit without overwhelming the server’s bandwidth.
In some cases, the crawling of sites might be causing a critical load on infrastructure, or cause unwanted costs during an outage. To alleviate this, one may decide to reduce the number of requests made by Googlebot.
Reduce crawl rate with Search Console (recommended)
If you want to quickly reduce the crawl rate, you can do so on the Crawl Rate Settings page by filling in a special request.
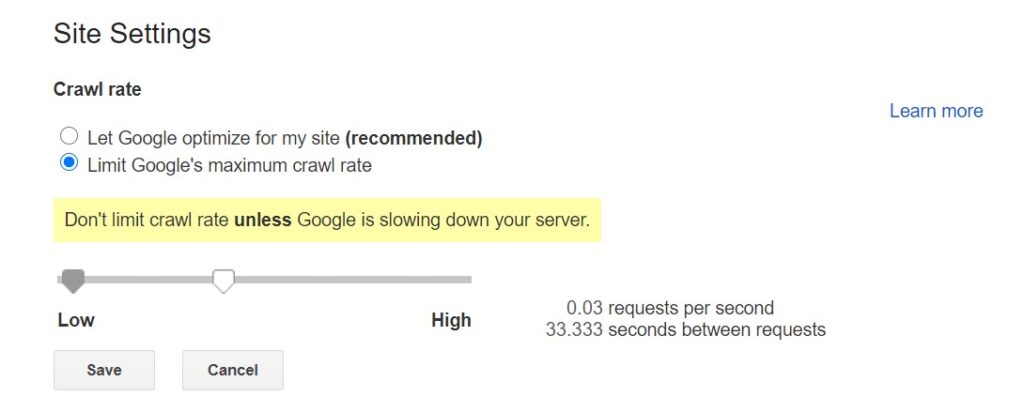
Changes made here will take place within a few days. However, be careful not to set the crawl rate value too low for your website’s needs. In 99% of cases, you don’t need to use that setting as Google knows how to adjust the crawl rate without overwhelming your server.
Let Google reduce the crawl rate automatically
If you need the crawl rate reduced urgently within a few hours or a day, then you can return an error page with a 500, 503, or 429 HTTP code.
Googlebot will reduce your site’s crawl rate once it encounters a big enough number of URLs with the 500, 503, or 429 HTTP codes, like when you disable your website.
The change is reflected in both the crawling of the URLs which return those errors and the website overall. The crawl rate will automatically start to increase again once the number of those errors is reduced.
