Updated: June 9, 2023.
The Google Safe Browsing Guide: what it is, how it works, why you should care, and how important Safe Browsing is in the context of Google page experience signals.
About six out of ten people on the globe are active internet users. And a relatively small proportion of them take active measures or employ good cybersecurity practices. Yet only a tiny fraction of the total users are at risk when they use the internet.
That’s because background safety measures, such as Google safe browsing are in place.
In my guide to Safe Browsing, you will learn:
- what Safe Browsing is,
- how Safe Browsing works to protect you on a daily basis,
- why Google Safe Browsing is important,
- how Safe Browsing relates to SEO and other Google page experience factors,
- how to use Safe Browsing,
and more!
Feel free to use the overview below to jump straight to a specific section of the guide.

Google Safe Browsing
Let me now tell you what Safe Browsing is and how it works. Here is the official Google Safe Browsing website.
What is Google Safe Browsing?
Google Safe Browsing is a blacklist service that provides constantly updated lists of web resources containing phishing content or malware. All of the most popular internet browsers, such as Chrome, Firefox, or Safari use the lists provided by the Google Safe Browsing service to protect and warn their users.

Google launched Safe Browsing in 2007 to protect users and the web. Since then, it has been maintaining a list of unsafe sites. Its algorithms scan billions of URLs every day, and if any one of them has malicious links or content or contains malware, the URL is added to the unsafe list.
Your purpose is to make sure that your website is never added to the list!
How does Google Safe Browsing work?
Most people don’t realize how easy it is to get phished on the internet and reveal sensitive information to malicious entities (that use social engineering to ensnare you). And that’s because most phishing links and harmful sites are “shot dead” in their tracks by nothing other than Google Safe Browsing.
This Google service literally protects from the shadows and keeps over four billion devices safe every day.
Have you ever clicked a link to a dangerous site where instead of going to the website, you were greeted with a bright red screen, warning you that there is a “deceptive site ahead” and that visiting it may be harmful to your device?
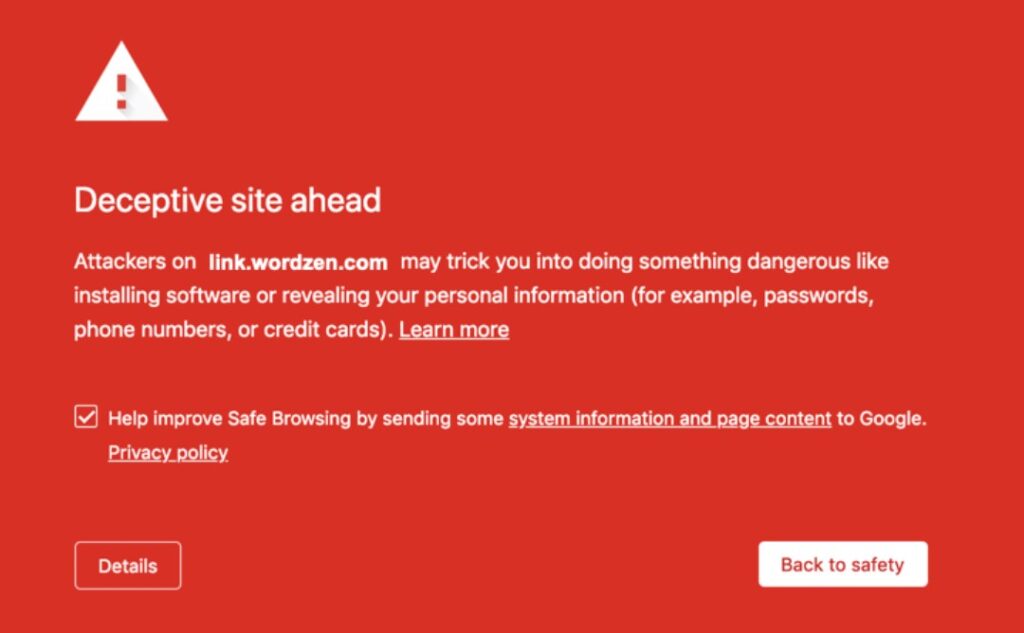
That’s essentially how Safe Browsing works to protect you. But there is much more to it.
- When you search for something, the safe browsing algorithms check to see if any of the unsafe URLs or web pages are part of the results. If you click one of the unsafe URLs, safe browsing flashes a warning.
- For legitimate websites, the Google team coordinates with webmasters to determine why their website was deemed unsafe by algorithms and what can be done to ensure the security of their users.
- The safe browsing service protects internet users from clicking harmful links (and entering a dangerous site), and downloading dangerous and unwanted software by giving them timely warnings.
- This layer of safety also covers social engineering attacks (like phishing) and malware (harmful software/code) downloads.
Quite brilliant, isn’t it?
You can learn more about Google Safe Browsing warnings here.
What Google Products use Safe Browsing?
Safe Browsing is available on the following Google products:
- Google Chrome: Google’s primary browser use safe browsing to ensure that internet users are browsing safely. It’s also available with other browsers (Safari, Firefox, Vivaldi, and GNOME).
- Google Search: Whether you execute a search from Chrome on your computer or using one of your other devices (voice search on phone or Alexa), the search results will be protected.
- Gmail: Safe search algorithms ensure that their users’ emails don’t contain any dangerous links to dangerous sites.
- Android: A lot of user data and important information is routed through android applications. If a user tries to download an application that’s not verified by Google play (directly from a link, usually from an unverified site), safe browsing warns its users. Thanks to this wider security net, even android users who want to experiment with unverified open-source android applications are protected.
- Google Ads: Paid ads are prominently displayed on web searches and safe browsing ensures that users who click on these ads are not directed to corrupt pages or a dangerous website.
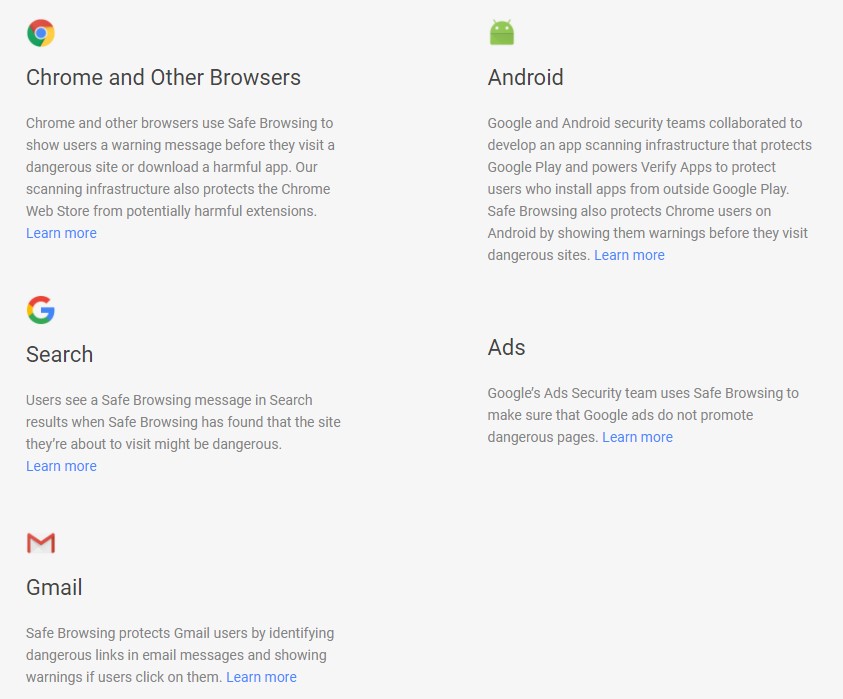
Safe Browsing permeates a lot of internet activity because the bulk of the activity is routed through browsers that come with safe browsing. It’s just one cybersecurity layer, and even if it’s a very porous layer, it keeps a lot of harmful sites, threats, bad web pages, malware, and unwanted software away.
What Browsers use Safe Browsing?
But it is not only Google products that use Safe Browsing. The following internet browsers also use lists provided by the Google Safe Browsing services:
Microsoft Edge uses its own Microsoft Defender SmartScreen which is a similar service to Google Safe Browsing.
Google Safe Browsing as a page experience signal
As I am an SEO and SEOSLY is a website about SEO, I need to look at Google Safe Browsing from an SEO perspective.
Here is what you should know about Google Safe Browsing in the context of SEO:
- The safety and experience of users are two top priorities for Google.
- Safety is a very important component of a user experience.
- These two should be top priorities for you both as an SEO and a website owner
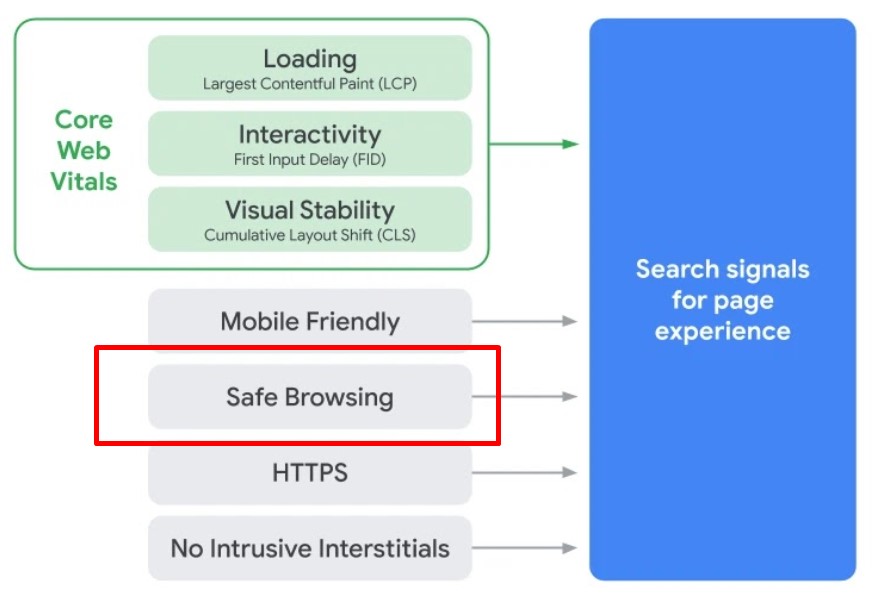
- Google Safe Browsing used to be one out of five Google page experience signals. It is no longer a page experience ranking factor. The remaining ones include Core Web Vitals (Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift) HTTPS (check HTTP vs HTTPS), Mobile-Friendly, and No Intrusive Interstitials.
- To learn more about the topic, make sure to check my Google page experience guide.
Your task, as a website owner or an SEO, is to make sure that your website is safe for its users and does not contain malware. If you fail to do that, then Google will put a red flag on your site and add it to the Safe Browsing blacklist of unsafe URLs.
If that happens, you will not only fail to meet an important Google page experience factor, but your website will become invisible for most internet users. I believe you get the point!
You can use the Safe Browsing site status to check how Google sees your website.
Let’s check how my website is doing! This is what you want to see for your website.
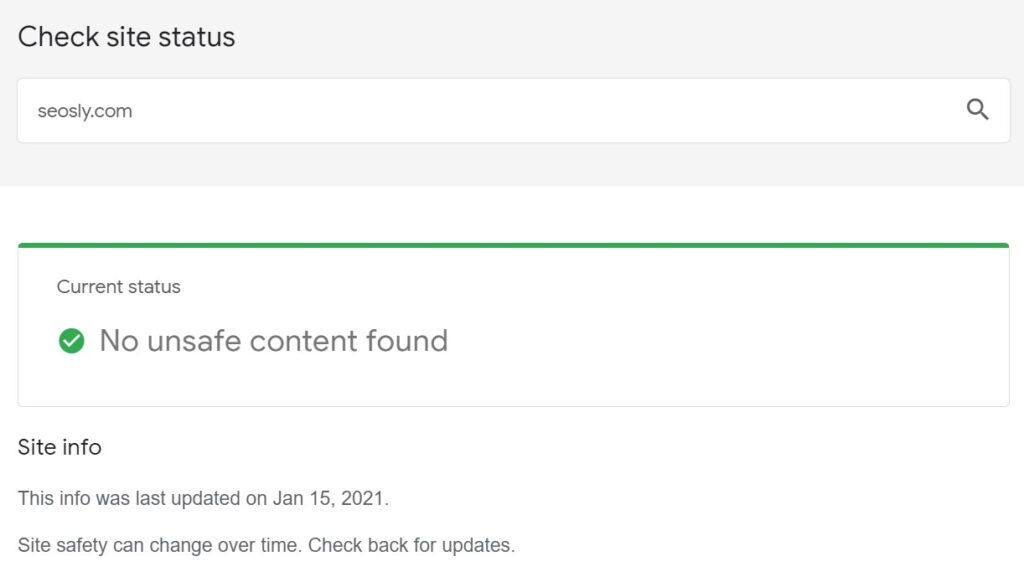
How to use Google Safe Browsing
Even though it automatically saves protects over 4 billion devices that browse the web every day (powerful growth from 3 billion devices in 2017), you still need to know how to use Safe Browsing.
Google Safe Browsing check
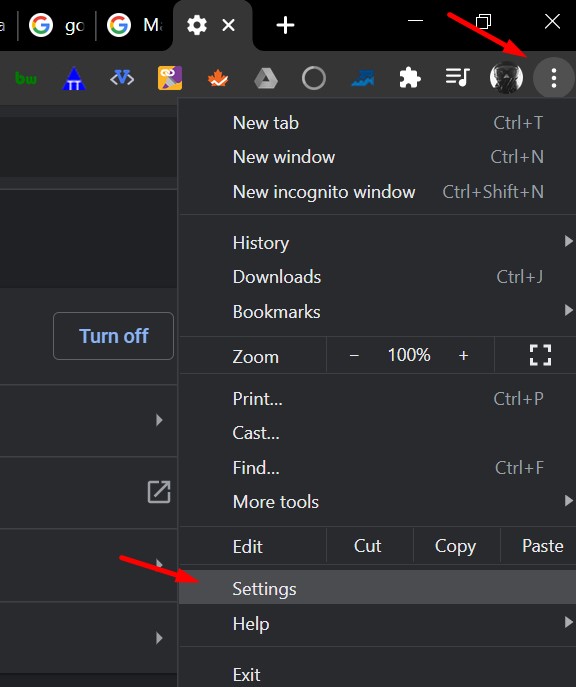
The Safe Browsing check is deceptively easy to execute when you are using Chrome. Simply click on the three dots and then settings.
You’ll find a settings box labeled safety check. You can also choose to jump to it using the appropriate tab on the top-left corner.
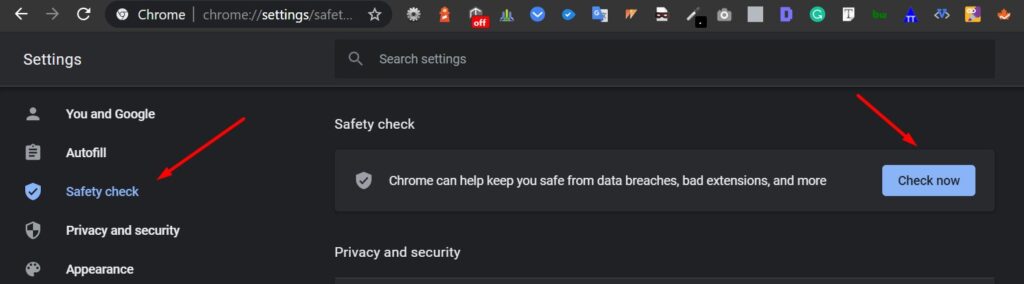
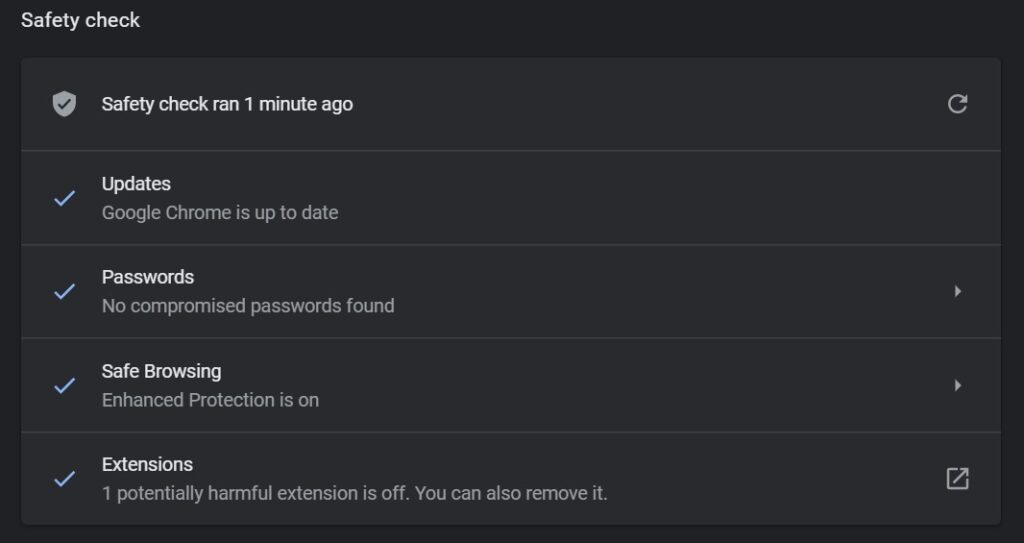
Click Check now to start the Safety check.
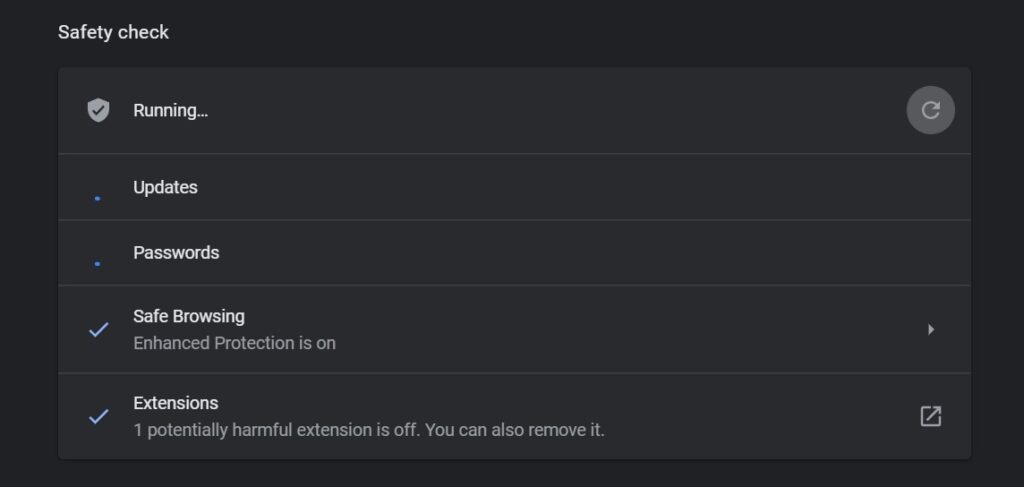
When you hit the Check now button, it executes for checks:
- Whether Chrome is updated or not.
- Whether your passwords are safe or have been compromised (you have to be logged in for that).
- Whether safe browsing is on or not (and which protection tier is it on Standard/Enhanced).
- Whether your Chrome extensions are safe.
When complete, you should see something like this.
Okay, but what if you want to turn off Safe Browsing? Let me show you how to do it.
How to turn off Google Safe Browsing
Though it’s not recommended that you turn off safe browsing on Chrome, you may do so quite easily from the Safety check setting. Here is what to do:
- Execute the Safety check (like you did in the step above).
- Click on the Safety check result.
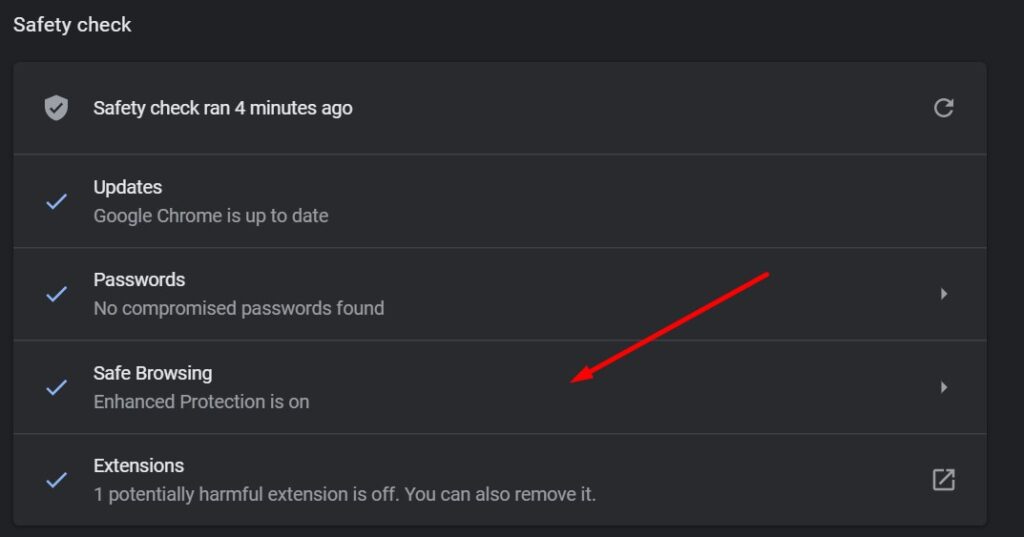
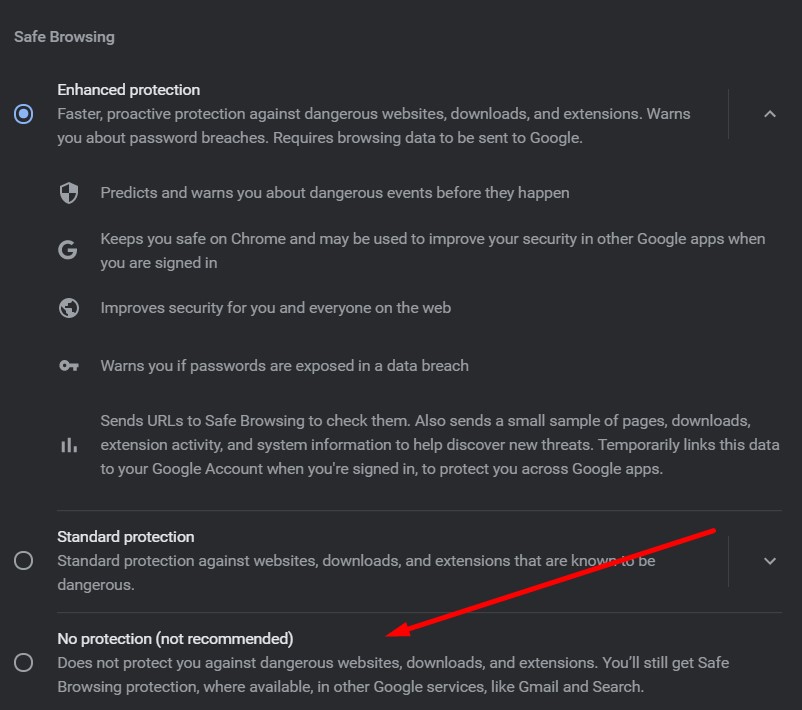
- Choose the “no protection” option.
- Confirm your choice.
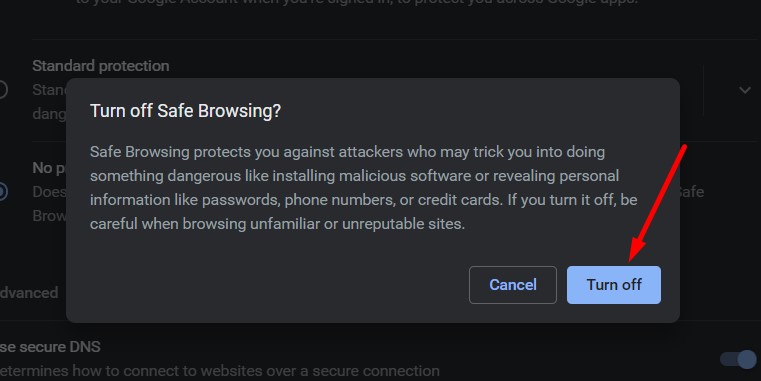
Note that this is not recommended for the majority of users. You may want to turn off Google Safe Browsing if you want to, for example, get rid of a warning for a website you are doing some development work on and to do debugging.
How to turn on Google Safe Browsing
You may turn on Chrome Safe Browsing by following the steps stated above and selecting either the “Standard protection” or “Enhanced protection” option. Alternatively, you can click on the security setting within the privacy and security settings to turn on safe browsing on the settings page.
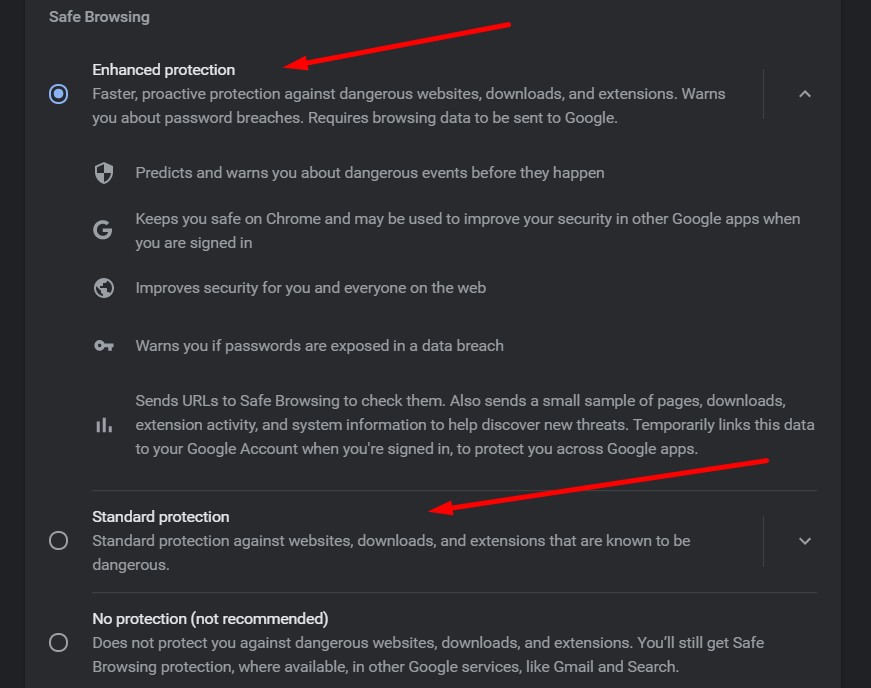
Note that by default Safe Browsing is turned on.
Two Chrome Safe Browsing modes
The Safe Browsing service comes with two different options you can use to protect your internet activity and for browsing safely.
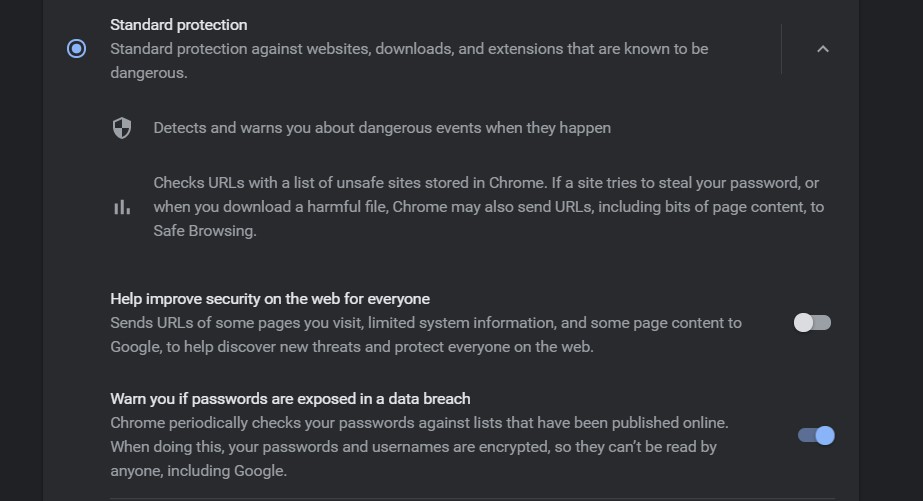
Standard Safe Browsing
It’s the default safety setting that’s turned on from the first time you download Chrome on any of the devices. It ensures you don’t click on malicious sites. The same protection applies across multiple devices that use a product that comes with safe browsing.
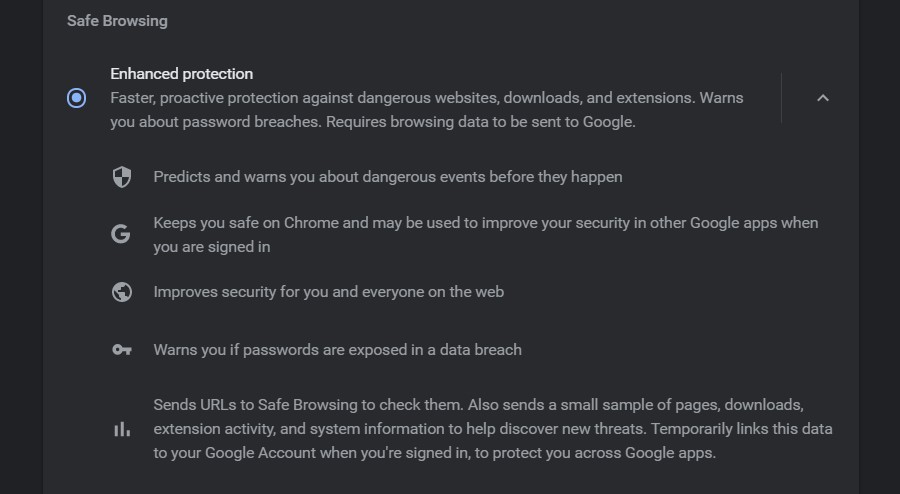
Enhanced Safe Browsing
It adds to the layer of standard safety and automatically warns you about password breaches and sends Google additional information about you, and the data is linked, so you are protected across all devices.
The core feature of checking links across lists of malicious sites remains the same, no matter which protection tier is used or on which device it’s used.
Safe Browsing Warnings
The warnings you see from the safe browsing may vary based on the potential trap you may be wandering into. The Safe Browsing warnings usually fall within the below five categories:
- The site contains malware. These sites will want to install malware on your computer when you visit them.
- A deceptive site. Websites on lists for phishing or social engineering attacks.
- A suspicious site. The site seems to be suspicious.
- A site with harmful programs. These sites may want you to install harmful programs.
- A site is loading scripts from unauthenticated sources. These sites are not secure.
- A dangerous site. These sites are in warning lists for containing malware or unwanted software attached to their pages (from the first day or added later, they get added to the lists either way).
You will also like these guides:
