Updated: June 9, 2023.
In this short guide, I will show you how to add a sitemap to Google Search Console in a few simple steps & share with you a few powerful tips.
The sitemap of your website is the essential roadmap for search engines. Not only does it help Google and other search engines discover all the web pages of your site, but it also helps prioritize what should be crawled and indexed first.
Google Search Console allows you to submit an XML sitemap and check whether Google is able to crawl it properly.
Let me quickly show you how to do it.

How to add a sitemap to Google Search Console (step by step)
Here is what you need to do to submit a sitemap to Google Search Console:
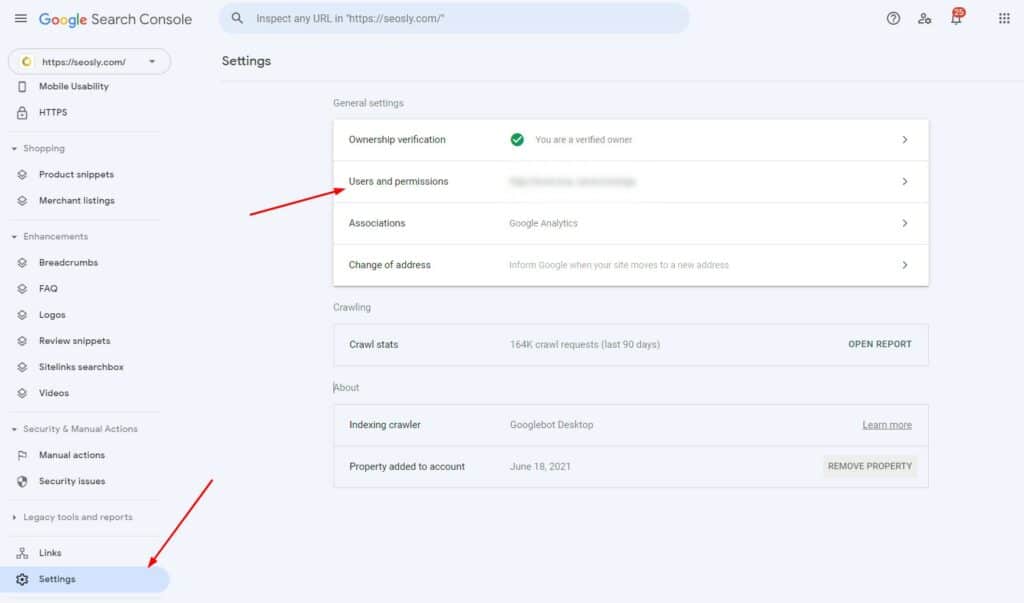
1. Log in to Google Search Console. Make sure you have the correct level of access. You need to be either the owner or have full access (check my guide on how add and remove users from Google Search Console).
You can check the access level of users under Legacy tools and reports > Settings > Users and permissions.
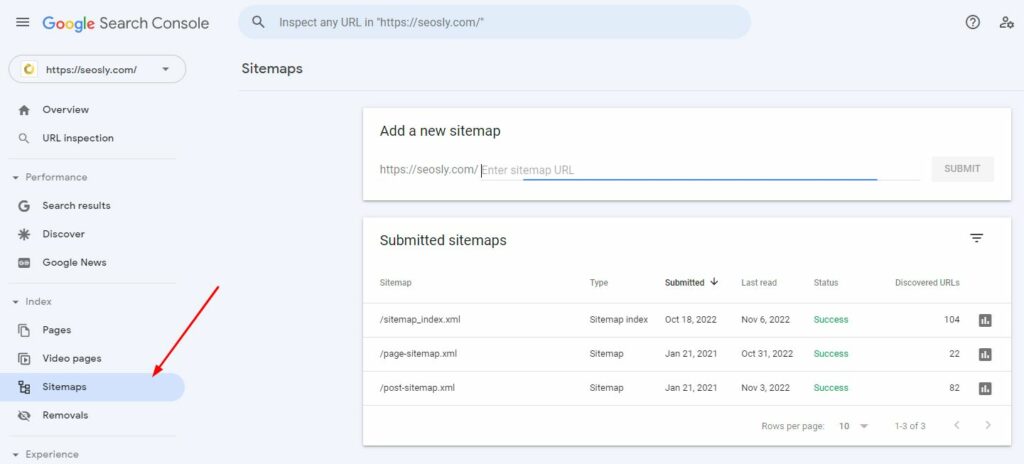
2. Under Index, navigate to Sitemaps.
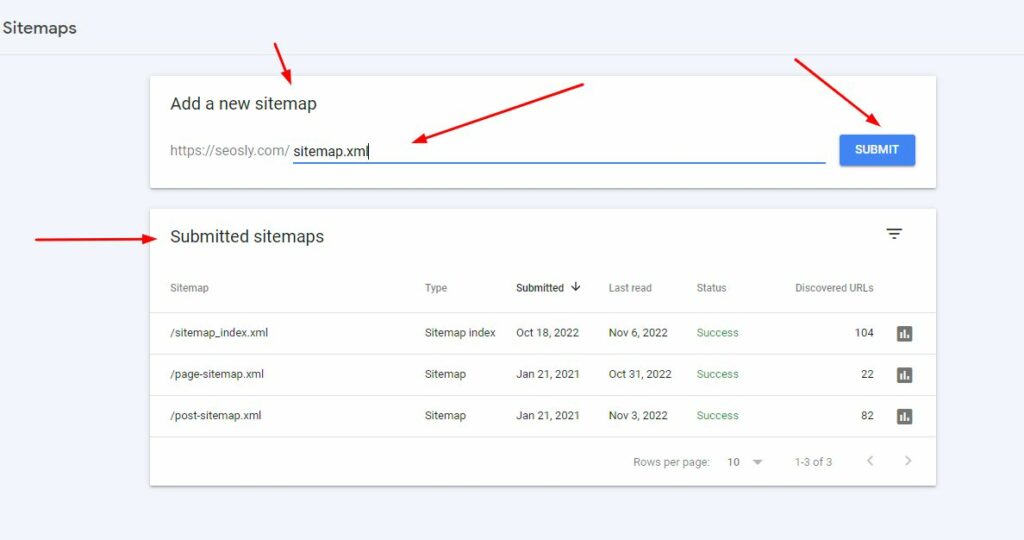
3. Below Add a new sitemap, paste the URL of your sitemap and hit SUBMIT. If a sitemap has already been submitted, you will see it under Submitted sitemaps.
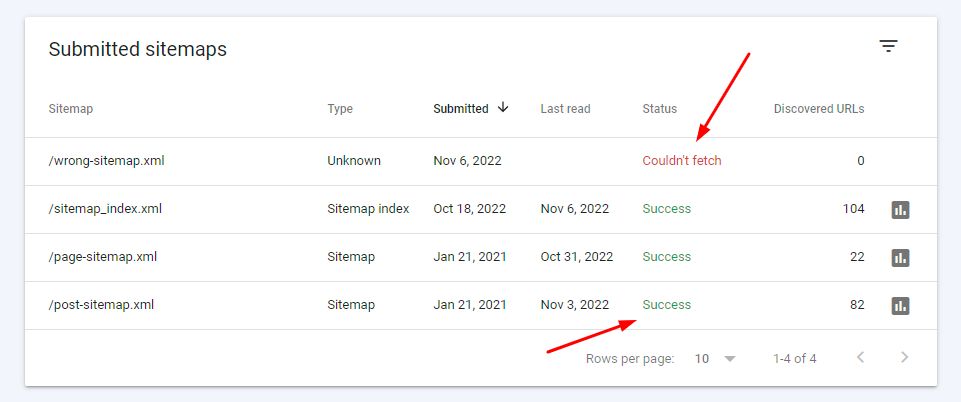
4. Once you submit the sitemap, you will see its status under Submitted sitemaps. You should see Success and the number of URLs under Discovered URLs. If you see Couldn’t fetch under Status, then Google was unable to read your sitemap.
5. Click on the submitted sitemap to see more details, such as Last read, Discovered URLs and whether it has been processed successfully (you can see that in the preview as well).
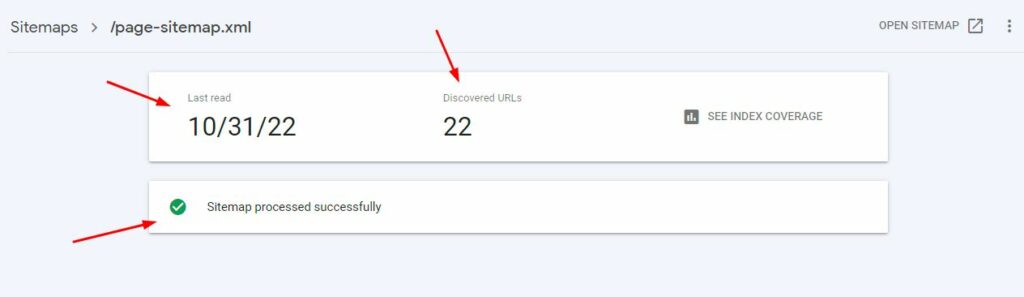
6. Click on SEE INDEX COVERAGE to check how many of the pages submitted have actually been indexed by Google. This step is a crucial step for SEO.
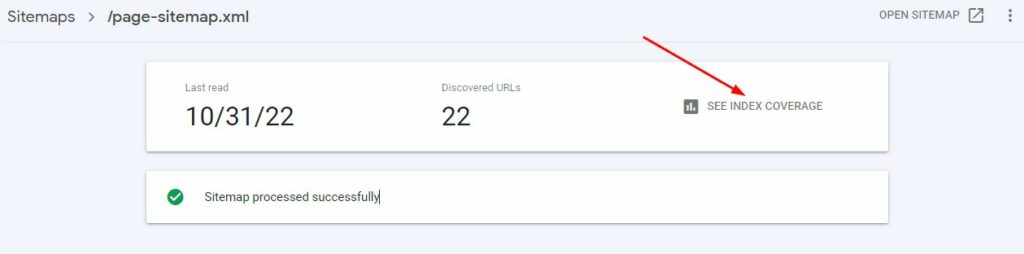
If you have submitted the correct URLs (see below), then you want to see all of them indexed.
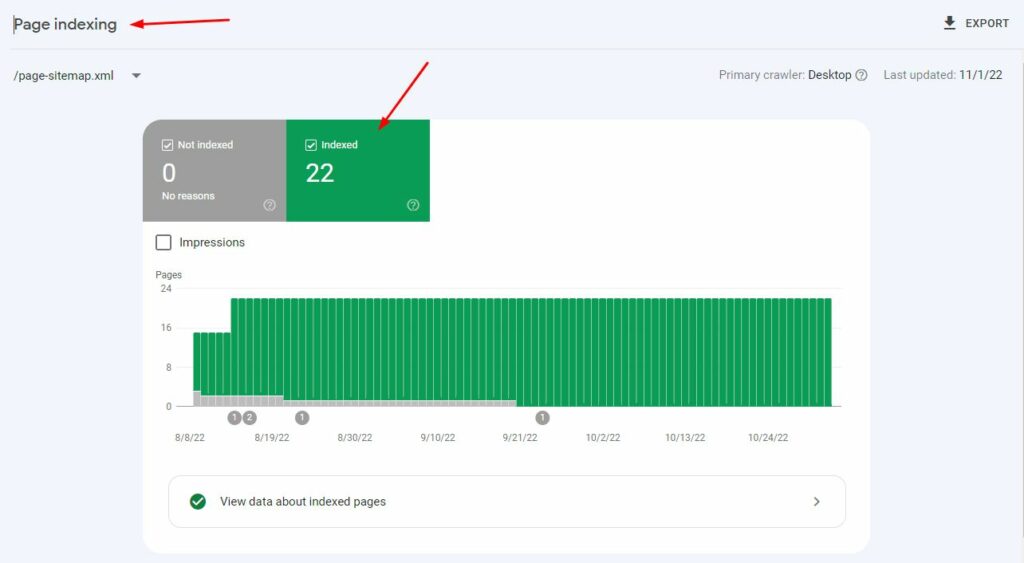
If they aren’t indexed, you should investigate why this is the case. Under Why pages aren’t indexed, you will see possible reasons.
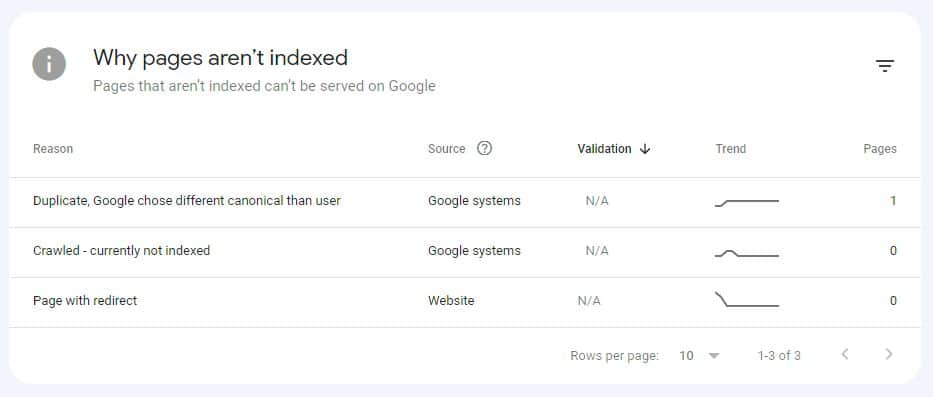
💡Note that often pages listed under Crawled – currently not indexed may have quality issues. Remember that Google is not obliged to index all your pages.
What pages should you submit in a sitemap?
A sitemap should only contain the URLs that you want to be indexed and displayed in search results. Make sure the URLs you submit are indexable, canonical and consistent (if your site uses www, submit all URLs with www).
What pages you should not submit in a sitemap?
Don’t submit pages that are non-indexable, redirected or blocked in robots.txt. Also, don’t submit ULRs with session IDs or user identifiers.
Frequently asked questions about adding a sitemap to Google Search Console
Here are a few FAQs and considerations that are quite important.
Do you have to submit a sitemap to Google Search Console?
It is not obligatory to submit a sitemap to Google Search Console. Google will still be able to crawl your site and find the sitemap, especially if it is in a standard location or/and is indicated in robots.txt.
Why should you add a sitemap to Google Search Console?
You should add a sitemap to Google Search Console if you want to see when Google last read your sitemap or whether it had problems fetching it. It is generally a good SEO practice to submit a sitemap to GSC.
When it is important to submit a sitemap to Google Search Console?
If you have a huge website (with millions of pages or tens of thousands of frequently updated pages), then you should definitely submit a sitemap to GSC (and have sitemap in the first place). Not only will you be able to see if Google has fetched it correctly, but you will also help Google prioritize what to crawl and potentially optimize your site’s crawl budget.
What happens if I remove the submitted XML sitemap from Google Search Console?
Don’t worry. Nothing will happen! It won’t remove the sitemap from Google. Google will still know about your sitemap and will be visiting it. If you removed the sitemap by accident, you can resubmit it as shown above.
What type of sitemap can you add to Google Search Console?
Google supports the sitemap formats, such as XML, RSS, mRSS, Atom 1.0, and Text. The types of pages you can indicate in your sitemap include HTML pages, videos, images, and news.
Basically, there are two main types of sitemaps you can have:
- XML sitemaps which are meant for search engine robots. XML sitemaps should be either put in the standard location like
/sitemap.xmlor indicated in robots.txt. The standard location can also point to the sitemap index if there are mutiple sitemaps on the website like in the case of my site.
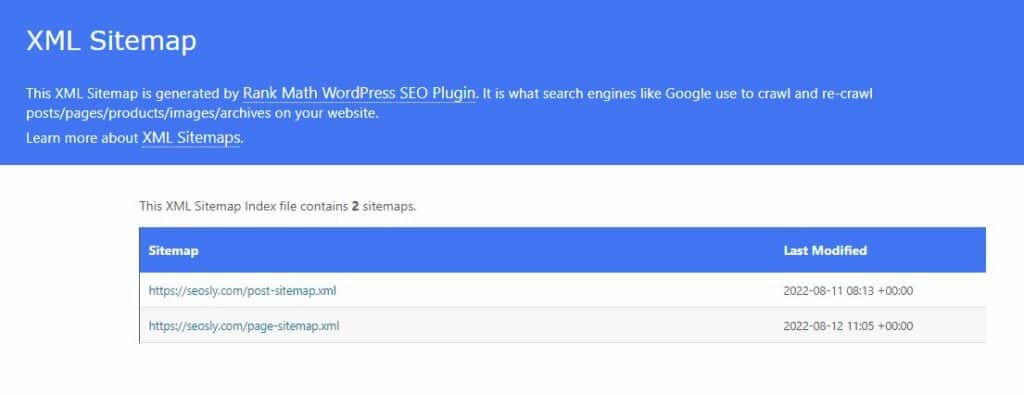
- HTML sitemaps which are meant for people. An HTML sitemap is simply an HTML page that lists the webpages of the website and also indicates their hierarchy.
It is important not to confuse XML sitemaps with HTML sitemaps. As noted above, Google Search Console does not support HTML sitemaps. Instead, it only supports a sitemap that is in one of the following formats:
- XML (the most popular)
- RSS, mRSS, and Atom 1.0
- Text
You can learn more about sitemaps in the official Google documentation on sitemaps.
What are the limits for the sitemaps submitted to Google Search Console?
A single sitemap (regardless of its format) should not exceed 50MB (without compression) and 50K URLs. If it exceeds these limits, you should split your sitemap into multiple sitemaps and list them all in the sitemap index.
How to find the sitemap of your website?
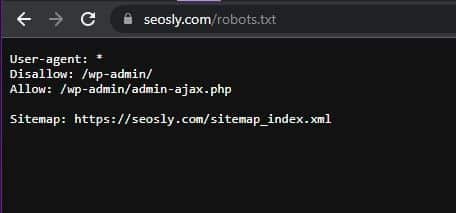
In most cases, the sitemap of the website can be found in one of the standard locations like /sitemap.xml, /sitemap_index.xml (which is the index of the sitemaps), or /sitemap/ (which often redirects to sitemap.xml).
If the sitemap is not in a standard location, then there is a chance it is indicated in robots.txt.
Make sure to check my in-depth guide on how to find the sitemap of website. It lists all possible ways of finding a sitemap.
I hope this article helped you. Share it with your friends and other SEOs if you like it. Thank you.
You may also like these similar articles:
