Updated: June 9, 2023.
Here is the list of 25+ Yandex search operators & search tips that will make you a more efficient Yandex user.
Yandex search operators (or search parameters) are special commands you type into the search box together with your search query to get more relevant and detailed results.
Search operators are not unique to Yandex, of course. They work with other search engines, such as Google or Bing as well. However, search operators differ slightly from search engine to search engine.
In this guide, I’m taking a closer look at the Russian search engine and showing you a bunch of interesting Yandex search tips.
I personally tested each search operator from the list, took my own screenshots, and shared my insights with you. Let’s dive deep into the Yandex advanced search.

Even though Google has about 92% of the search engine market share worldwide, its market share in Russia amounts to “only” 58%, with 40% belonging to Yandex.
Take a look at the stats below.
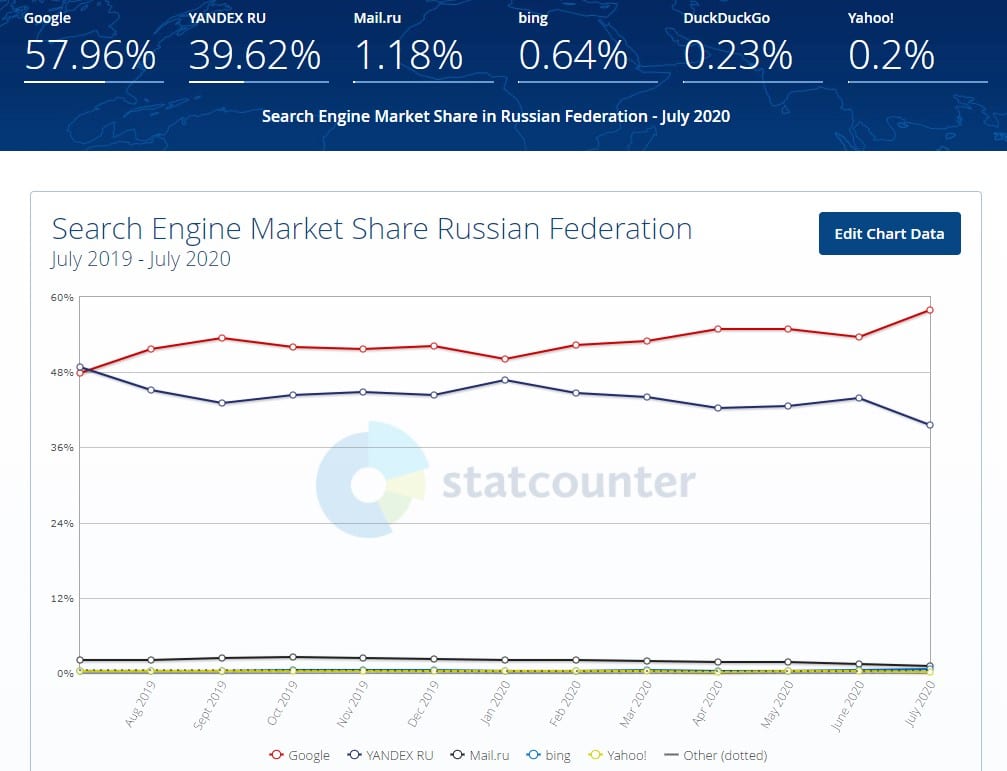
With the above in mind, it’s still worth knowing what search operators work with Yandex and how to use them correctly.
15+ Yandex Search Operators
Here are basic Yandex Boolean search operators (or search parameters) that let you refine your search to:
- look for specific forms of the word (gender, case, number, etc.),
- look for specific parts of speech (verb, noun, adjective, etc.),
- exclude certain terms from your search,
- create complex search commands returning highly specific results.
The symbols ❌ and ✔️ will let you know if a given search operator works with Google or Bing.
☝️ The chances are you are also a Google and Bing user, so I invite you to check my list of Bing search operators.
+ (Plus)
+ lets you search for web pages containing the term preceded by it. Note that you can use + multiple times in one query to include multiple terms in the search results.
+
Example: audit +seo
Example: audit +seo +free

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 This Yandex Boolean search operator as used in the example above will return web pages that relate to the word “audit” and definitely contain the word “seo” (the first example) or both the word “seo” and “free” (the second example).
⚡ Taking about audits, make sure to check my guide on how to do an SEO audit.
– (Minus)
- lets you find web pages that don’t contain the term preceded by -. The excluded term should be placed at the end of your search query. You can use - multiple times in one query to exclude more terms.
-
Example: seo -audit
Example: seo -audit -buy

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 This search query will return web pages that relate to the term “seo” but don’t contain the word “audit” (the first example) or both the word “audit” and “buy” (the second example).
“” (Quotation Marks)
"" lets you find web pages containing the exact words in the form and order specified in quotation marks.
""
Example: "mobile seo audit"

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 This search will return web pages that contain the phrase in quotes.
* (Asterisk)
* acts as a wildcard operator and will fill the missing word or suggest a relevant term depending on the other terms used in the search query. The asterisk works with the "" operator only. You can use multiple * to include more missing words.
*
Example: "the best seo *"

Example: "website * seo audit"

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 This Yandex search operator will return web pages containing the exact words from the quote with the inclusion of the missing word. The results the first example returned included, for example, “best SEO companies”, “best SEO firms”, “best SEO courses”, or “best SEO tools”.
Remember that this search operator is separated by spaces.
| (Pipe)
| will look for web pages that contain any of the terms specified. This is the Boolean OR operator. You can use | multiple times in one query.
|
Example: seo | sem | ppc

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 The above example search query will return web pages containing any of the words specified (seo, sem, or ppc). This Boolean operator is similar to the OR Google operator.
~~ (NOT)
~~ will exclude web pages that contain the term preceded by ~~. This is simply used as the Google NOT operator.
~~
Example: seo ~~audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 In the example above the search results will include the web pages that are about “seo” but don’t contain the word “audit”.
~
~ will exclude web pages in which the term preceded by ~ occurs in one sentence. The web pages containing the keywords in other sentences won’t be excluded.
~
Example: seo ~audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 This Yandex Boolean search operator is very useful if you don’t want to exclude the second term entirely but you don’t want it to be connected with the main term. In the example above I don’t want to find results that contain the phrase “seo audit” in one sentence but I don’t want to exclude the word “audit” entirely.
! (Exclamation Mark)
! lets you search for web pages containing the term in the form specified. Note that you can use ! multiple times in one query to find web pages containing multiple keywords.
!
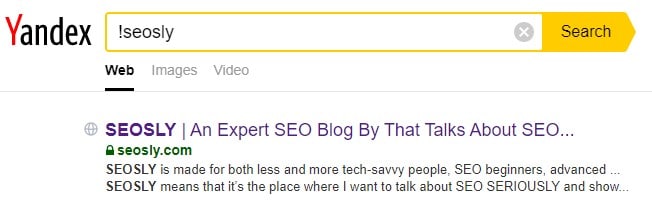
Example: !seos

Example: !seosly

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 This Yandex Boolean search operator will find web pages containing the term “seos” (the first example) in the form as specified without similar word search or any sort of extended search. The second example will let me check if my website has been indexed by Yandex.
You can use ! to include stop words like “and” which are ignored by default.
!! (Double Exclamation Mark)
!! will search for the dictionary form of the keyword.
!!
Example: !!seo

✔️ Bing
❌ Google
💡 This Yandex Boolean operator will let you find the dictionary definitions of the term specified. It works similar to the define: command that works with Google and Bing.
&
& will look for web pages that contain the words specified in one sentence.
&
Example: free & seo & audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
Google and Bing return more or less relevant results because they consider & a stop word and ignore it. For Google and Bing, it’s like simply typing the query free seo audit without quotation marks.
💡 This Boolean search operator is very useful for finding the web page containing the specified word or words all in one sentence.
&& or <<
&& will look for web pages containing the terms specified in one document (one web page). This search command is a bit broader than & which looks for words in one sentence.
&&
Example: seo && audit && free && technical

Example: seo << audit << free << technical

❌ Google
❌ Bing
Google and Bing return relevant results because they consider && or << to be a stop word and ignore it.
💡 This Yandex Boolean search operator will look for web pages that contain all the keywords specified.
/+n
/+n will look for web pages based on the closeness of the keywords specified. The number after the slash defines the word distance between the phrase before the slash and the phrase after the slash.
This search operator lets you perform very precise and detailed searches.
/+n
Example: seo /+2 audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
Google and Bing return more or less relevant results because they consider this parameter a stop word and ignore it.
💡 In this example, the search will return web pages in which the word “audit” appears 2 words after “seo”. It’s a bit similar to the AROUND Google operator and the NEAR Bing operator.
/-n
/-n works in the opposite “direction” to /+n and will find web pages relating to the keyword specified in which the keyword preceded by /- is the specified number of words apart in the left direction. This search command also lets you do very precise and detailed searches.
/-n
Example: audit /-2 technical

❌ Google
❌ Bing
Google and Bing return more or less relevant results because they consider this Yandex operator a stop word and ignore it.
💡 In this example, the search will return web pages in which the word “technical” appears 2 words before “seo”.
&&/n
&&/n will look for web pages in which the keyword and the offset keyword exist in one sentence. n defines how many words after the first term the second term must appear.
&&/n
Example: seo &&/2 audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
Google and Bing return more or less relevant results because they consider &&/n a stop word and ignore it.
💡 The Yandex Boolean search operator in the example will look for web pages containing the word “seo” and the word “audit” which appears two words after the word “seo”.
/(x y)
/(x y) will look for web pages in which the keyword specified appears within the range specified by x and y. x stands for the left offset from the keyword specified and y defines the right offset.
/(x y)
Example: seo /(-3 +3) audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
Google and Bing return more or less relevant results because they consider this parameter a stop word and simply ignore it.
💡 This Yandex Boolean search operator will find web pages with keywords “seo” and “audit” within the word range specified. In this case, it’s going to be the word “audit” which is 3 keywords to the left and 3 keywords to the right from the word “seo”.
()
() will help you group different keywords and operators in a complex query.
()
Example: seo && (+auditing | !audit)

✔️ Bing
✔️ Google
This is a Boolean operator that works with any search engine.
💡This Yandex Boolean search operator lets you create advanced and complex queries like the one in the example above.
10+ Advanced Yandex Search Operators
And here is the list of Yandex advanced search operators and commands that will perform specific searches and let you refine your search even further.
url:
url: will look for web pages with a specific URL address. Note that the address isn’t case sensitive. You should put the URL in quotation marks if it contains characters, such as ‘ " ( ) _.
url:
Example: url:seosly.com

✔️ Bing
❌ Google
💡 This search command will look for the URL of my website, that is, seosly.com
You can use * as a wildcard to find web pages with addresses starting with the value specified.
Stick to this format: url:host category/subcategory/*
Example: url:moz.com/blog/*

❌ Bing
❌ Google
💡 This search command will look for the web pages in the /blog category at moz.com.
inurl:
inurl: will look for web pages containing the word or words specified in their URL address.
inurl:
Example: inurl:seo

✔️ Bing
✔️ Google
💡 This search operator works pretty much the same in all search engines.
site:
site: will look for the web pages and subdomains of the website specified.
site:
Example: site:seosly.com

✔️ Google
✔️ Bing
💡 This search command will find all the indexed web pages and subdomains of the website seosly.com.
domain:
domain: will look for the web pages of the domain specified. This works with domains ending in “com”.
domain:
Example: seo domain:seosly

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 This search command will find the web pages containing the word “seo” that are located on the “.com” domain specified.
host:
host: will search for web pages that are hosted on the host specified. It is identical to the url: search operator if you only specify the hostname.
You need to stick to this format: host: www.second-level-domain.top-level-domain
Example: seo host:www.seosly.com

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 This search command will return web pages that contain the word “seo” and are hosted on the seosly.com domain.
rhost:
rhost: works the same as host: except that with rhost: the hostname must be written in the reverse order (starting from the top-level domain).
You need to stick to this format: rhost: top-level-domain.second-level-domain.www
Example: seo rhost:com.seosly.www

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 If you are comfortable writing URL addresses backward,then you will like this Yandex search operator.
If you place * at the end of the URL, then rhost: will search by the subdomains of the domain specified.
Example: seo rhost.com.moz.*

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 The search command from the first example will return the web pages that contain the word “seo” and are hosted at seosly.com. The second command will return web pages that contain the word “seo” and are hosted on all the subdomains of the moz.com domain.
title:
title: will look for web pages with the keyword specified in the title.
title:
Example: title:seo audit

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 The Yandex search command in the example above will look for web pages containing the phrase “seo audit” in the title. This is the equivalent to the Google intitle: search parameter.
mime:
mime: will look for specific file types in search results based on the keyword specified.
mime:
Example: seo mime:pdf

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 In the example above I want to search Yandex for PDF files relating to the phrase “seo”.
This search operator is the equivalent of the Google filetype: that also lets you find specific file types among search results.
lang:
lang: will look for web pages that are in the language specified.
The languages supported by Yandex include Russian (ru), Ukrainian (uk), Belarusian (be), English (en), French (fr), German (de), Kazakh (kk), Tatar (tt), Turkish (tr).
lang:
Example: seo lang:en

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 This search command will return web pages that contain the word “seo” and are in English.
date:
date: lets you filter web pages by their last modified date. You must specify the year while the day or month may be replaced with *.
To look for web pages with the specified last modified date, use the format date:YYYMMDD.
To look for web pages with the last modified date within the range, use the format date:YYYMMDD..YYYYMMDD.
To look for web pages whose last modified date is before or after the specific date, use the format:date<YYYMMDD. The available modifiers here are < <= > >=.
If you don’t have the full date, use the format date:YYYY**.
date:
Example: seo date:20200815 (modified on 8/15/2020)

Example: seo date:20200815..date:20200101 (modified between 8/15/2020 and 1/1/2020)
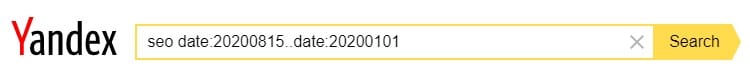
Example: seo date:>20200303 (modified after 3/3/2020)

Example: seo date:2020** (modified in 2020)

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 This Yandex search operator is very useful if you are looking for web pages from specific dates or date ranges. However, note that Yandex is not so quick in indexing web pages so if the date specified is today or yesterday the results may not be very relevant.
$ anchor()
$ anchor() will look for web pages that have the term specified in () in the anchor text of links.
$ anchor()
Example: $ anchor(seo)

❌ Google
❌ Bing
💡 The example Yandex-only search command will find web pages containing the expression within the anchor text of links.
I am not entirely convinced if this search command provides relevant results. Anyway, I’m mentioning it mostly for educational purposes.
Recommended Further Reading On Yandex Search Operators
Of course, I needed to do a bit of research to (hopefully) find and show you all the Yandex advanced search parameters that are there. Below are links to some valuable resources on the topic straight from Yandex:
- https://yandex.com/support/direct/keywords/symbols-and-operators.html
- https://yandex.com/support/search/query-language/search-operators.html
Make sure to check my other articles with search operators:

And what about this? (2017 year!) https://webmaster.yandex.ru/blog/izmeneniya-v-yazyke-zaprosov
Thanks, Ivan. I will check that.