Updated: June 30, 2023.
A super quick guide on how to check if a page is indexed (in three simple ways).
Ever wondered how Google knows about your latest blog post or the new product page you just added? It’s all about indexing.
Simply put, indexing is the process where search engines like Google add a page into their giant database.
Think of it as Google’s way of acknowledging your web page’s existence. But why is it important?
Well, if your page isn’t indexed, it might as well be invisible to Google. It won’t show up in the search results, no matter how great your content or your SEO strategy is.
So it’s crucial to ensure your web pages are properly indexed.
In this quick guide, I will show you three ways of checking if a page is indexed. I will also briefly discuss reasons why a page may not be indexed and offer possible fixes.
Let’s get started.

TL;DR: How to check if a page is indexed
If you don’t have time to read the entire article, here is the gist for you.
- Google Search Console (recommended): Add your website to Google Search Console (if you haven’t already done it!) and use the ‘URL inspection’ tool. Enter your webpage URL and it will tell you whether it’s indexed or not.
- Use Google’s “site:” search operator: Enter “site:yourwebpageURL” into Google’s search bar. If your page appears in the search results, it’s (most likely) indexed.
- Indexed Pages Checker Tools: Use online tools like Semush or SE Ranking to check the indexing status of your webpage.
Remember, if your page is not indexed, it won’t appear in Google’s search results. So make sure all your important pages are indexed!
What is indexing and why it is important
Indexing is the search engine’s method of storing and retrieving data efficiently. It works like the index in the back of a book (hence the name), which provides a quick way to find specific content.
When it comes to SEO, indexing is a vital first step. It’s the process where search engines like Google crawl your website, analyze your web pages, and add them to their database.
Once your page is indexed, it’s eligible to show up in the search results and attract all those lovely organic visitors we’re after.
In the grand scheme of things, indexing is your page’s ticket to the show, the show being Google’s search results.
Without a ticket, your page won’t even be considered, regardless of how top-notch your content may be.
That’s why understanding indexing, and ensuring your pages are indexed, is fundamental to your success in SEO.
Methods to check if a page is indexed
Here are the three main ways of how to check if a page is indexed.
URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console
The most reliable and recommended method for checking if your page is indexed is by using Google’s own Search Console. Here’s how:
- Go to the Google Search Console and log in.
- Select your website from the list.
- Find the ‘URL Inspection’ tool on the left-hand menu.
- Enter the URL of the page you want to check.
- Google will then fetch the page and show you the current indexing status.
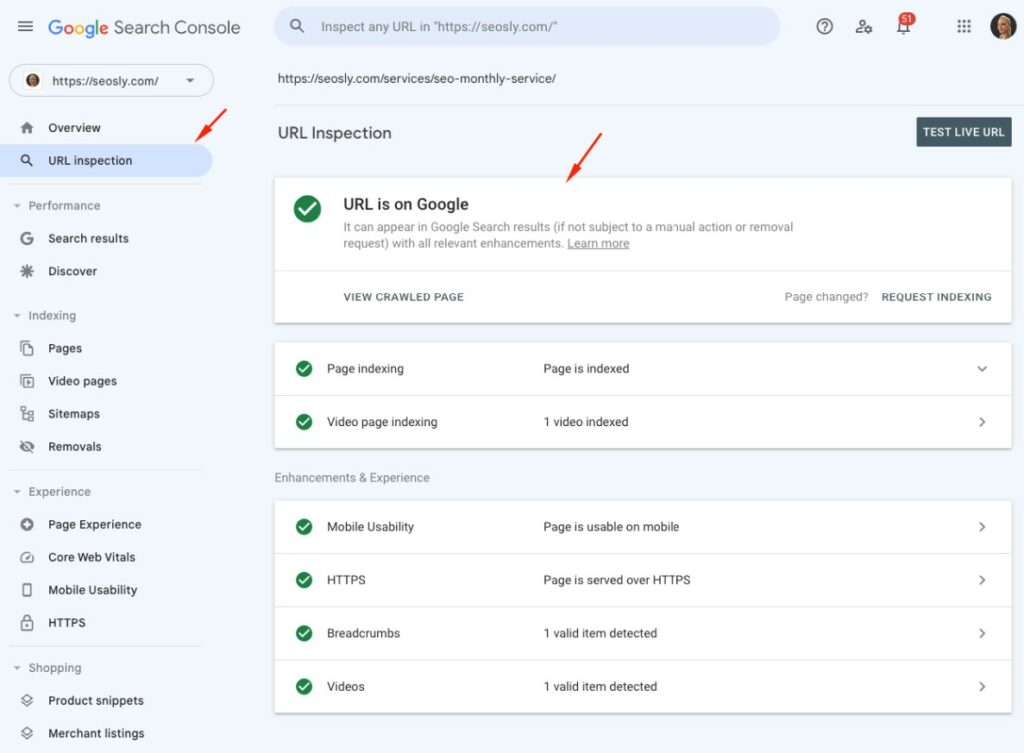
The results will clearly state whether the page is on Google or not. If it says “URL is not on Google”, this means your page is not indexed. However, if it says “URL is on Google”, your page is indexed.
Keep in mind, this method requires access to the Google Search Console for the website you’re checking. If you don’t have it, you won’t be able to use this method.
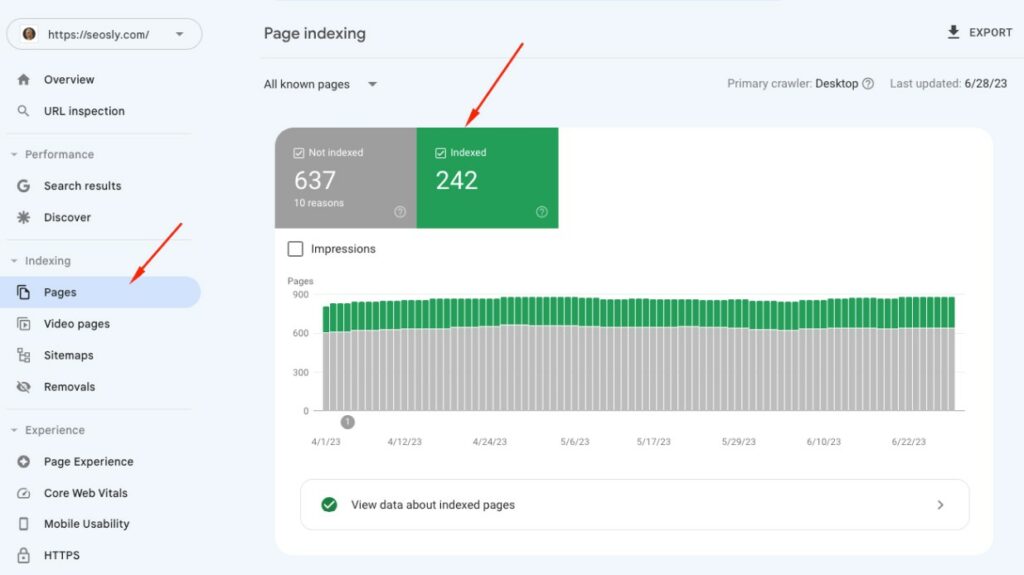
TIP: If you want to check the overall number of pages indexed (and not indexed), use the Indexing report (to go ‘Indexing’ > ‘Pages’).
Site: search command
You can use the “site:” command directly on Google search to check if a page is indexed. Here’s how:
- Open Google.com.
- Type “site:” followed by your page URL in the search bar (e.g., site:yourwebsite.com/yourpage).
- Press enter.
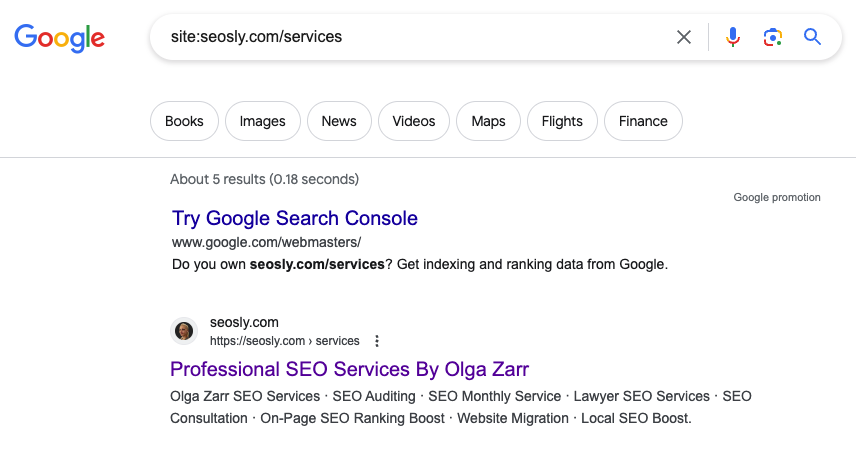
If your page appears in the search results, it’s likely indexed. If not, it’s probably not indexed. But be warned: this method is not foolproof.
NOTE: Google doesn’t always show all indexed pages with this command, and it may show pages that are not indexed at all. This method is most useful for sites where you don’t have access to Google Search Console.
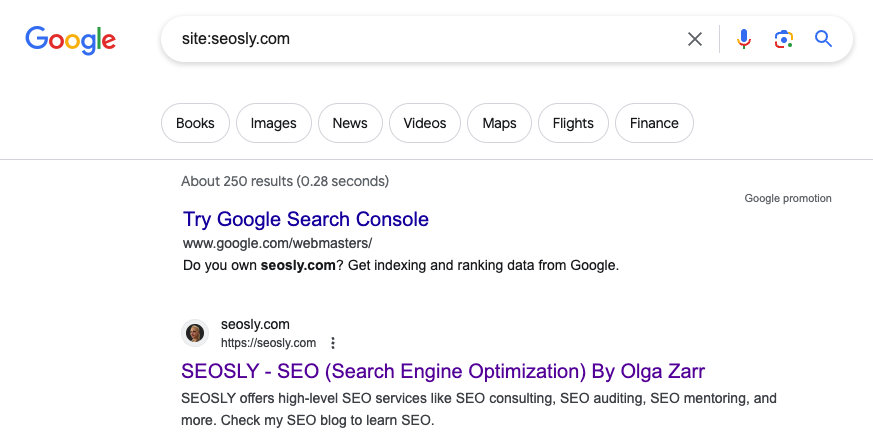
Check my list of Google search commands to perform advanced Google searches like the site: command.
Indexed pages checker tools
Tools such as Semrush, SE Ranking, Ahrefs or Moz can help you find out if a page is indexed. These tools are not as reliable as Google Search Console, but they can give you a general idea.
- Log into your chosen tool.
- Enter your website’s URL.
- Navigate to the ‘Indexed Pages’ section or use a similar function.
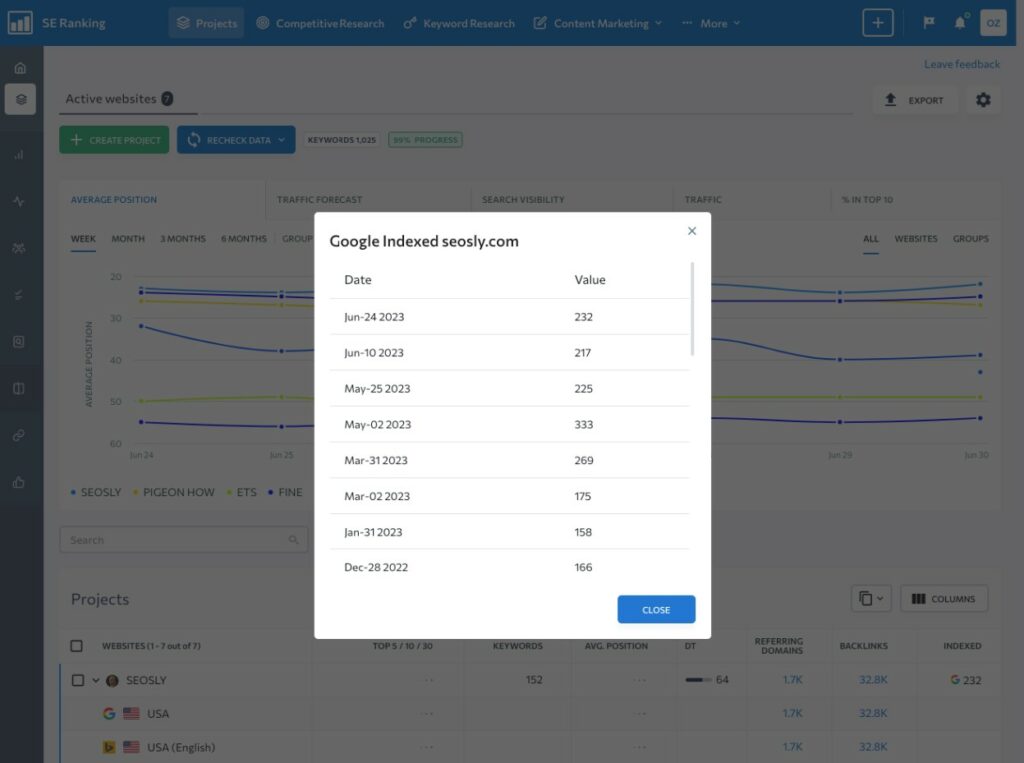
While these tools can help, always remember that they are only estimates and the data might be outdated or not 100% accurate. Use them as part of your overall SEO toolkit, but don’t rely on them for the final word on indexing.
What to do if your page is not indexed
Finding out your page isn’t indexed can be a bit of a bummer. But don’t panic, there are things you can do:
- Check your robots.txt file: Make sure that you haven’t inadvertently blocked Googlebot from crawling your page.
- Inspect your meta tags: Ensure there’s no “noindex” tag on your page. This tag tells search engines not to index a page.
- Review your sitemap: Is the page included in your sitemap? If not, add it. Sitemaps help Google find and understand your content. While in smaller sites sitemaps are not important, they become crucial for large or super large sites.
- Request indexing in Google Search Console: If your page is crawlable and doesn’t have a “noindex” tag, go to Google Search Console, use the URL Inspection tool, and click on ‘Request Indexing’. This prompts Google to crawl and index your page.
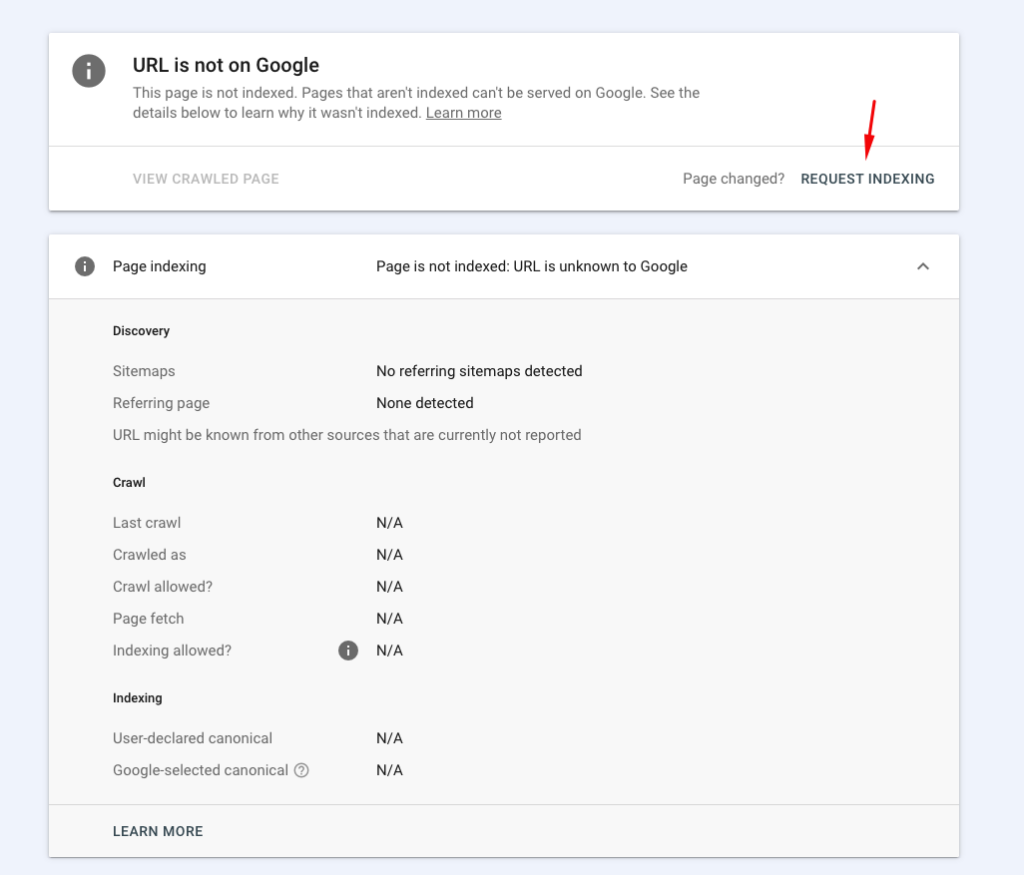
Remember, indexing takes time. It may take days or even weeks for Google to index your page.
Common reasons why a page might not be indexed
Here are a few reasons why your page might not be indexed:
- Page is blocked by robots.txt: If your page is blocked in the robots.txt file, Google may not index it. Review your robots.txt file and make any necessary changes.
NOTE: This may prevent your page from being indexed or if a page gets indexed, it will be displayed in search results together with “Indexed but blocked in robots.txt” ugly information. - Page has a “noindex” meta tag: This tag tells search engines not to index a page. If this tag is present, remove it to allow indexing.
- Page isn’t included in the sitemap: Google uses your XML sitemap to find and understand your content. If your page isn’t included, it might not be indexed.
Check my guide on how to audit XML sitemaps. - The page is new: It can take time for Google to find and index new pages. Be patient and give it a few days. The newer the site overall, the longer it will take Google to index its pages.
- The page has low-quality or duplicate content: Google strives to index high-quality, unique content. If your page has low-quality or duplicate content, it might not be indexed.
In that case, you might get stuck in “Crawled – currently not indexed” or “Discovered – currently not indexed” in Google Search Console.
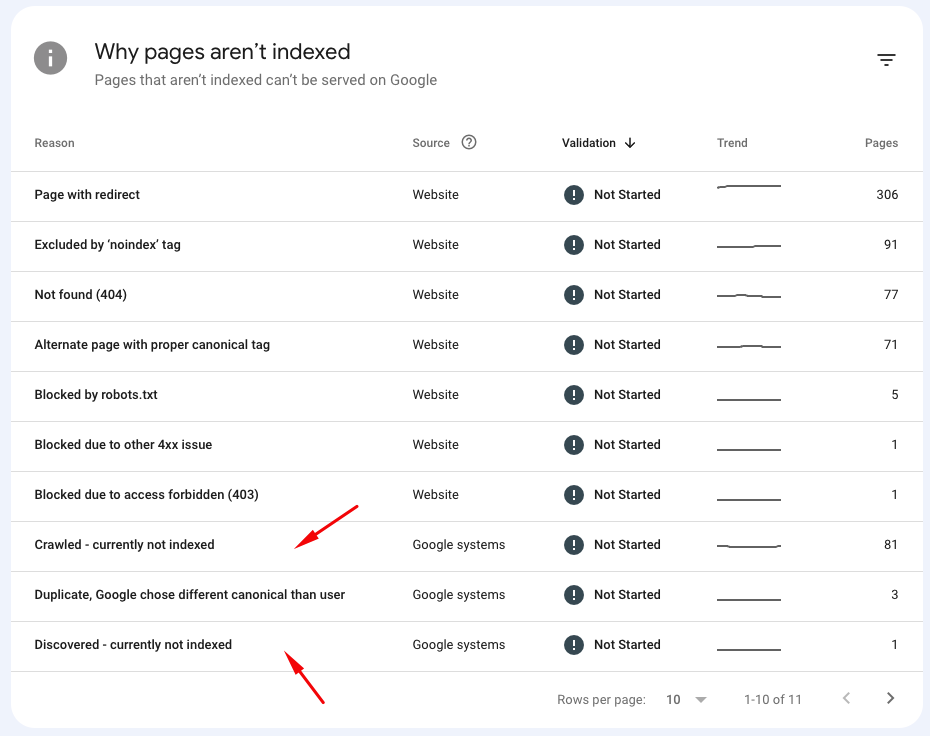
Remember, these issues are fixable. Review your website and its content, make the necessary changes, and request indexing in Google Search Console. Stay patient and persistent, and before you know it, your page will be indexed!
And taking about the reasons why a site/page is not indexed, I strongly recommend you listen to this episode of the Search Off the Record podcast.
Final thoughts & tips on checking if a page is indexed by Google
Checking whether your webpage is indexed is an essential step in the SEO process. It confirms that Google has crawled your site and included your page in its search results.
If you find your page isn’t indexed, don’t panic. Instead, check your robots.txt file, inspect your meta tags, review your sitemap, and request indexing in Google Search Console.
If the page is not indexing due to issues like a blocked page, “noindex” meta tag, absence from the sitemap, being too new, or containing low-quality or duplicate content, address these issues and then request indexing.
Remember, SEO is a marathon, not a sprint (it is a runner speaking here). Be patient, persistent, and before you know it, your page will be showing up in those search results, ready to attract clicks and conversions! 😎
